- Home
- >
- Triangle Sum Theorem – Explanation & Examples
JUMP TO TOPIC
Triangle Sum Theorem – Explanation & Examples
 We know that different triangles have different angles and side lengths, but one thing is fixed — that each triangle is composed of three interior angles and three sides that can be of the same length or different lengths.
We know that different triangles have different angles and side lengths, but one thing is fixed — that each triangle is composed of three interior angles and three sides that can be of the same length or different lengths.
For instance, a right triangle has one angle that is exactly 90 degrees and two acute angles.
Isosceles triangles have two equal angles and two equal side lengths. Equilateral triangles have the same angles and same side lengths. Scalene triangles have different angles and different side lengths.
Even though all of these triangles differ in angles or side lengths, they all follow the same rules and properties.
In this article, you’ll learn about:
- The Triangle Sum Theorem,
- Interior angles of a triangle, and
- How to use the Triangle Sum Theorem to find the interior angles of a triangle?
What is the Interior Angle of a Triangle?
In geometry, the interior angles of a triangle are the angles that are formed inside a triangle.
Interior angles have the following properties:
- The sum of interior angles is 180 degrees (Triangle Angle Sum Theorem).
- All interior angles of a triangle are more than 0° but less than 180°.
- The bisectors of all three interior angles intersect inside a triangle at a point called the in-center, which is the center of the in-circle of the triangle.
- The sum of each interior angle and exterior angle is equal to 180° (straight line).
What is the Triangle Angle Sum Theorem?
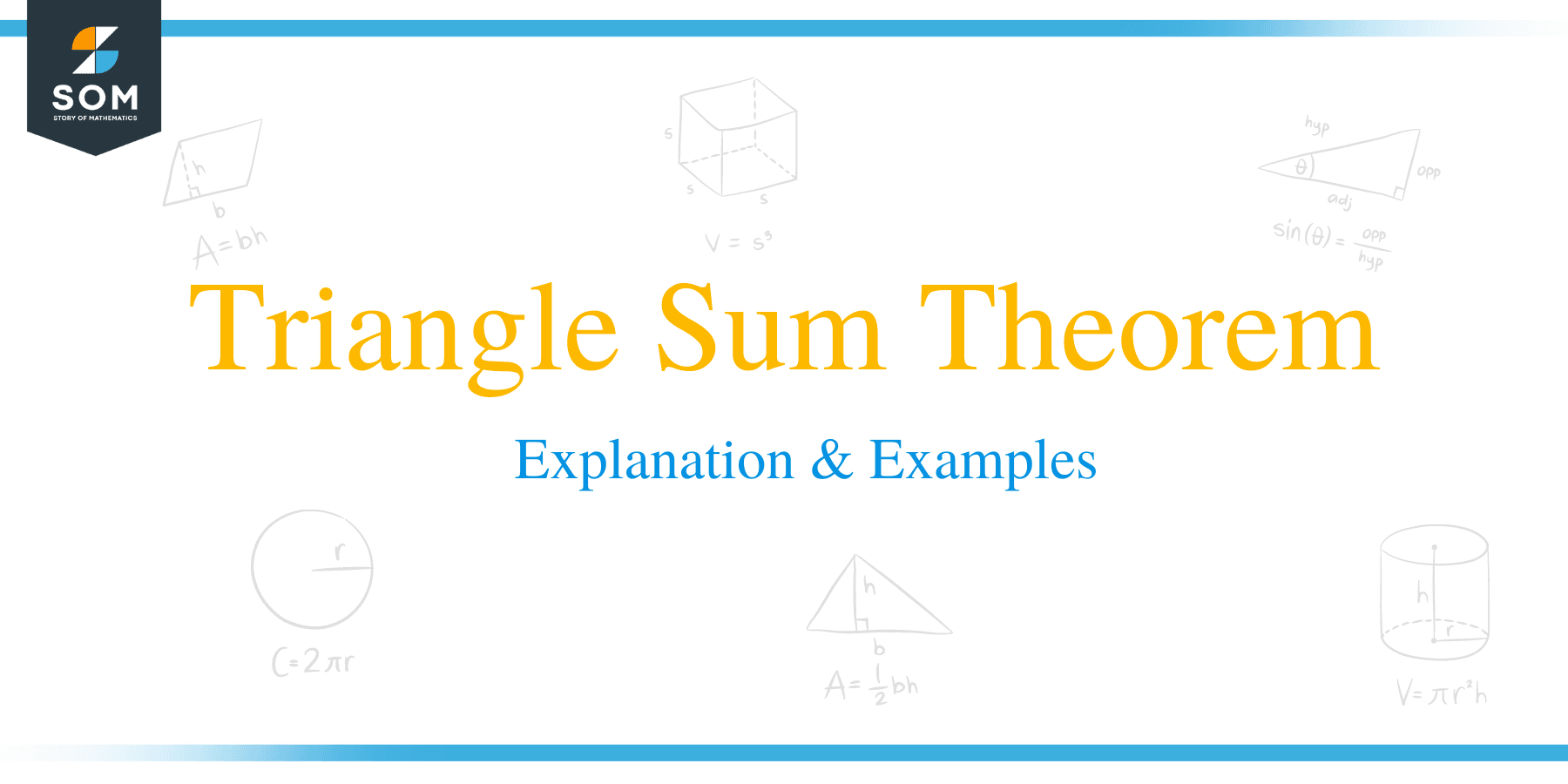
One common property about triangles is that all three interior angles add up to 180 degrees. This now brings us to an important theorem in geometry known as Triangle Angle Sum Theorem.
According to the Triangle Angle Sum Theorem, the sum of the three interior angles in a triangle is always 180°.
We can this as:
∠a + ∠b + ∠c = 180°
How to Find the Interior Angles of a Triangle?
When two interior angles of a triangle are known, it is possible to determine the third angle using the Triangle Angle Sum Theorem. To find the third unknown angle of a triangle, subtract the sum of the two known angles from 180 degrees.
Let’s take a look at a few example problems:
Example 1
Triangle ABC is such that, ∠A = 38° and ∠B = 134°. Calculate ∠C.
Solution
By Triangle Angle Sum Theorem, we have;
∠A + ∠B + ∠C = 180°
⇒ 38° + 134° + ∠Z = 180°
⇒ 172° + ∠C = 180°
Subtract both sides by 172°
⇒ 172° – 172° + ∠C = 180° – 172°
Therefore, ∠C = 8°
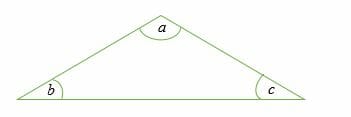
Example 2
Find the missing angles x in the triangle shown below.
Solution
By Triangle Angle Sum Theorem (Sum of interior angles = 180°)
⇒ x + x + 18°= 180°
Simplify by combining like terms.
⇒ 2x +18°= 180°
Subtract both sides by 18°
⇒ 2x + 18° – 18° = 180° – 18°
⇒ 2x = 162°
Divide both sides by 2
⇒ 2x/2 = 162°/2
x = 81°
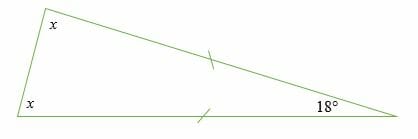
Example 3
Find the missing angles inside the triangle below.
Solution
This is an isosceles right triangle; therefore, one angle is 90°
⇒ x + x + 90°= 180°
⇒ 2x + 90°= 180°
Subtract both sides by 90°
⇒ 2x + 90°- 90°= 180° – 90°
⇒ 2x =90°
⇒ 2x/2 = 90°/2
x = 45°
Example 4
Find the angles of a triangle whose second angle exceeds the first angle by 15° and the third angle is 66° more than the second angle.
Solution
Let;
1ST angle = x°
2ND angle = (x + 15) °
3RD angle = (x + 15 + 66) °
By Triangle Angle Sum Theorem,
x° + (x + 15) ° + (x + 15 + 66) ° = 180°
Collect the like terms.
⇒ 3x + 81° = 180°
⇒ 3x = 180° – 81°
⇒ 3x = 99
x =33°
Now substitute x = 33° into the three equations.
1ST angle = x° = 33°
2ND angle = (x + 15) ° = 33° + 15° = 48°
3RD angle = (x + 15 + 66) ° = 33° + 15° + 66° = 81°
Therefore, the three angles of a triangle are 33°, 48° and 81°.
Example 5
Find the missing interior angles of the following diagram.
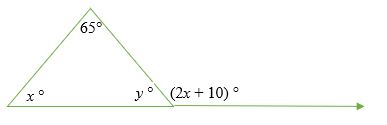
Solution
Angle y ° and (2x + 10) ° are supplementary angles (sum is 180°)
Therefore,
⇒ y ° + (2x + 10) ° = 180°
⇒ y + 2x = 170°……………… (i)
Also, by Triangle Angle Sum Theorem,
⇒ x + y + 65° = 180°
⇒ x + y = 115° ………………… (ii)
Solve the two simultaneous equations by substitution
⇒ y = 170° – 2x
⇒ x + 170° – 2x = 115°
⇒ -x = 115° -170°
x = 55°
But, y = 170° – 2x
= 170° – 2(55) °
⇒ 170° – 110°
y = 60°
Hence, the missing angles are 60° and 55°
Example 6
Calculate the value of x for a triangle whose angles are; x°, (x + 20) ° and (2x + 40) °.
Solution
Sum of interior angles = 180°
x° + (x + 20) ° + (2x + 40) ° = 180°
Simplify.
x + x + 2x + 20° + 40° = 180°
4x + 60° = 180°
Subtract 60 from both sides.
4x + 60° – 60°= 180° – 60°
4x = 120°
Now divide both sides by 4.
4x/4 = 120°/4
x = 30°
Therefore, the angles of the triangle are 30°, 50°, and 100°.
Example 7
Find the missing angles in the diagram below.
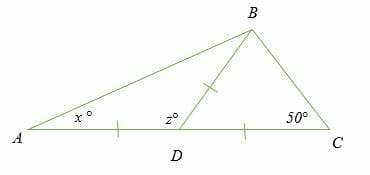
Solution
Triangle ADB and BDC are isosceles triangles.
∠ DBC = ∠DCB = 50°
∠ BAD = ∠ DBA = x°
Therefore,
50° + 50° + ∠BDC = 180°
∠BDC = 180° – 100°
∠BDC = 80°
But, z° + 80° = 180° (Angles on a straight line)
Hence, z = 100°
In triangle ADB:
z° + x + x = 180°
100° + 2x = 180°
2x = 180° – 100°
2x = 80°
x = 40°
