JUMP TO TOPIC
Factors of 99: Prime Factorization, Methods, Tree, and Examples
The factors of 99 are specified as every natural number that divides the said number, i.e., 99 entirely, produces a whole number in the quotient, and leaves zero as the remainder. Differently, the factors of 99 are explained as all the numbers multiplied by one another to produce the target number 99.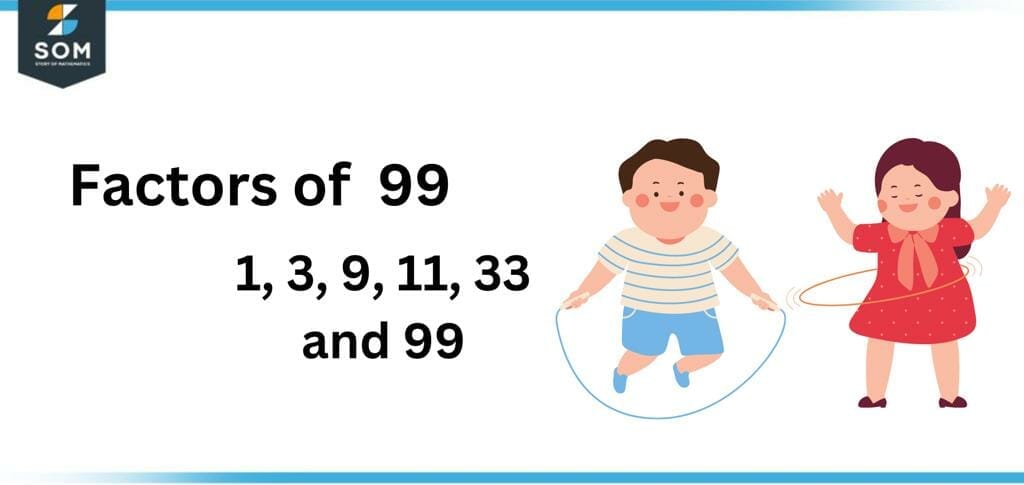
Figure 1 – All possible Factors of 99
What Are the Factors of 99?
The factors of 99 are 1, 3, 9, 11, 33, and 99.The number 99, an odd and a composite number, has six factors, as mentioned above. These numbers are the perfect divisors of the number 99, meaning they do not leave any remainder behind upon dividing the number 99.How To Calculate the Factors of 99?
You can calculate the factors 0f 99 by several methods: the division method, multiplication method, and prime factorization method.This article explains the calculation of factors of 99 by the commonly used division method. To begin with, the process of finding factors of 99 by this method divides 99 by the smallest natural number, which is 1.\[ \dfrac{99 }{1} = 99, r = 0 \]As 1 has perfectly divided the number 99 and left no remainder ( r = 0), 1 is a factor of 99. Now consider the following consecutive natural number in the count, the smallest even prime number (2), to find whether it is a factor of 99 or not.\[ \frac{99}{ 2} = 49.5 \ (\text{not a factor}) \]It is clear that 2 does not divide the number 99 completely and produces a fraction in the quotient. Hence, 2 is not a factor of 99.To find the rest of the factors of 99, divide 99 by the numbers and determine whether it is divisible completely or not. The division process is shown as follows:\[ \dfrac{99}{3} = 33, r = 0 \]\[ \dfrac{99}{9} = 11, r = 0 \]\[\dfrac{99}{11} = 9, r = 0 \]\[\dfrac{99}{33} = 3, r = 0 \]Now, divide 99 by itself as below:\[\dfrac{99}{99} = 1, r = 0\]From the method described above, the numbers which have wholly divided the number 99 without leaving any remainder behind are the factors of 99. The factors found through the above division method are 1, 3, 9, 11, 33, and 99.Key Features of Number 99
Here are some key features of the number 99 which should be recognized to understand and determine the factors of 99.- 99 is a natural number that is odd simultaneously.
- 99 is a composite number.
- 99 is not a perfect square.
- 99 is the largest two-digit number.
- The cross sum of 99 is 18.
- 99 has six divisors.
Interesting Facts
For further understanding of the factors of 99, the following information must be acknowledged.- The smallest factor of 99 is 1.
- The largest factor of 99 is the number 99 itself.
- All the factors of 99 are odd numbers.
- 99 has only two prime factors, which are 3 and 11.
- The sum of divisors of 99 is an odd composite number which is 156.
Factors of 99 by Prime Factorization
The prime factorization represents a composite number in the structure of the product of prime factors of the said composite number. The composite number is 99 in this case.Differently, it can be clarified as: the number 99 is represented as a multiplication of all of its possible prime factors; it is called the prime factorization of the number 99. The prime factorization has its basis of the division method, but the distinction is that this technique only uses prime numbers product to express the number 99.To recall the concept, the numbers with no divisors other than themselves and a universal divisor 1 are known as Prime Numbers. To begin with, the process of finding factors of 99 by prime factorization divides the number 99 by the smallest prime number that divides it entirely without leaving a remainder. Furthermore, the number produced as a result of the above-stated division is divided again by the smallest possible prime number. This process continues until the final quotient 1 is achieved, which cannot be split further into its multiples.The process is started by dividing the smallest prime factor by the given number 99, which in this case is 3.\[\dfrac{99}{3} = 33 \]The resultant number (33) acquired from this division is a prime number and can be divided by itself only.\[\dfrac{33}{3} = 11 \]The number generated as a result of the divide is 11, which is a prime number, and prime numbers are always divisible by themselves only.\[\dfrac{11}{1} = 1 \]Here, the final result achieved is 1, which cannot be divided any further, and the procedure stops here. The prime factorization of 99 can be expressed as:Prime Factorization = 3 × 3 × 11
The prime factorization of 99 can also be expressed as:\[ 99 = 3^2 \times 11 \]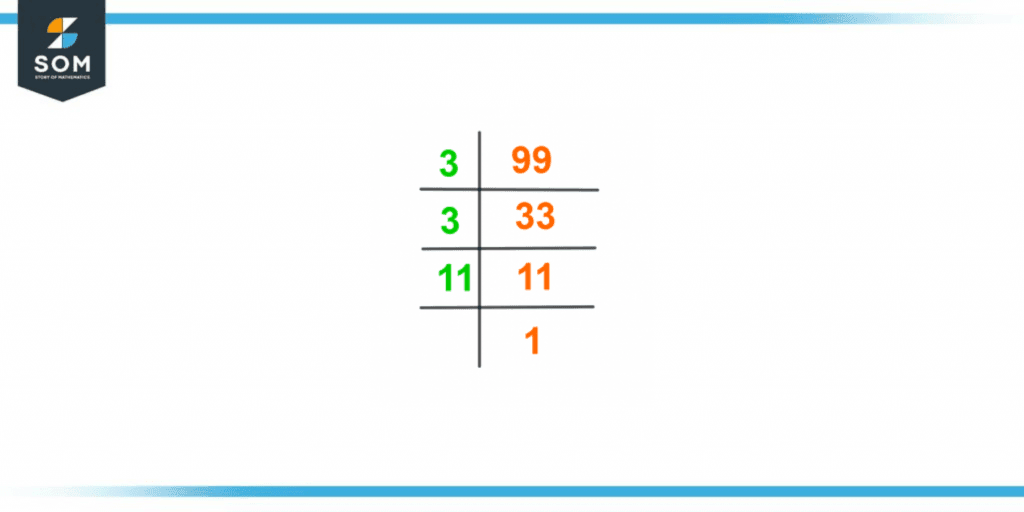
Figure 2 – Prime Factorization of 99
Factor Tree of 99
A factor tree is a unique method to find the factors of 99 using the diagram in the form of tree branches. The process utilizes the basic principles of prime factorization. For this purpose, the tree branching represents the division of the number under consideration.The process is shown in the form of a tree undergoing the branching procedure. The continuity of the branching depends on the presence of a composite number on either of the two branches resulting in the division.The splitting of numbers stops at the point where a certain split produces prime numbers on both of its ends.Considering the division rules by the factor tree method, we first write 99 into multiples for the given number. It would be:99 = 3 × 33
Secondly, divide the number 33 by its prime factor.33 = 3 × 11
As the division has produced both the prime numbers in this step. Hence, the procedure stops here after only the second divide.The factors tree of 99 is represented in figure 2.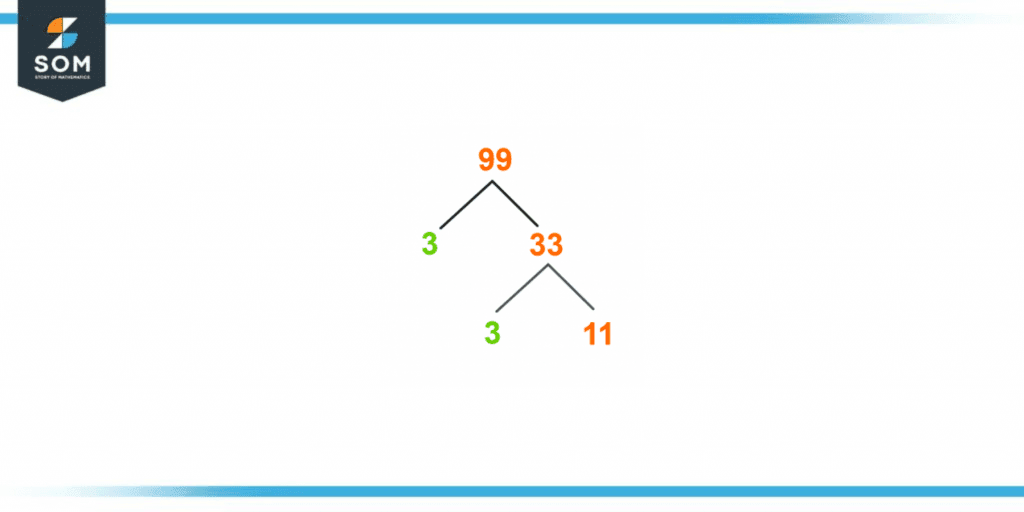
Figure 3 – Factor Tree of 99
Factors of 99 in Pairs
Factors of 99 in pairs are explained as the set of two integral numbers which multiply to produce the number 99.In other words, it is the presentation of the product of the factors of the number 99 in the form of pair of two numbers.1 × 99 = 99
3 × 33 = 99
9 × 11 = 99
The number 99 has only six factors in total which can be represented in sets of pairs as follows:(1, 99)
(3, 33)
(9, 11)
It is a universal fact that when a pair of negative numbers are multiplied together, they produce a positive integer. Hence additive inverse of all the factors of 99 can also be written in pairs. These are called negative pair factors of 99.The following mathematical equations can explain the negative pair factors of 99:(-1) × (-99) = 99
(-3) × (-33) = 99
(-9) × (-11) = 99
Therefore, the negative pair factors of number 99 are as follows:(-1, -99)
(-3, -33)
(-9, -11)
Important Points to Ponder
- Only integers and whole numbers can be the factors of a given number.
- Decimals and fractions cannot be represented in the form of factors as factors are produced by the complete division of a given number.
- The number of pair factors remains the same for a given number in both its positive and negative forms. The negative form is also called the additive inverse of the same number.
Factors of 99 Solved Examples
Example 1
What is the prime factorization of 99?Solution
The prime factorization of 99 can be shown asPrime Factorization of 99 = 3 × 3 × 11
The prime factorization of 99 can also be denoted as99 = 3$^2$ x 11
Example 2
Find the sum of factors of 99.Solution
The factors of 99 are 1, 3, 9, 11, 33, and 99.Sum of factors of 99 = 1 + 3 + 9 + 11 + 33 + 99
Sum of factors of 99 = 156
Images/mathematical drawings are created with GeoGebra.