What Is 1 3/5 as a Decimal + Solution With Free Steps
The fraction 1 3/5 as a decimal is equal to 1.6.
The mathematical concept of a Fraction is important. It helps in figuring out how many equal parts can be combined to form a whole object. Proper fractions, improper fractions, and mixed fractions are some of their key types.
The upper part of the fraction is called Numerator and the lower part of the fraction is called the Denominator.
Proper Fractions are those in which the denominator is greater than the numerator, whereas Improper Fractions are those in which the numerator is greater than the denominator. A fraction that is often created by combining a whole number with a proper fraction is called a Mixed fraction. And if the same number is repeating continuously then it’s called a recurring decimal number.
A fraction is simplified to obtain its decimal number, which includes a decimal point between the fractional and whole number parts.
We have a mixed fraction as 1 3/5 and let’s solve it by using the Long Division method.
Solution
As we know, our fraction is a mixed fraction type, so let’s first convert it into a fraction before division. Afterward, it can be classified as a proper or improper fraction. In our case, we just need to multiply the denominator 5 with the whole number 1 and then add it to the numerator 3. The given mixed fraction is equal to 8/5.
1+3/5 = 8/5
A numerator is called a dividend and a denominator is named a divisor so in this case 8 is divided by 5. Therefore the dividend and divisor of the above-mentioned simplified fraction are given as:
Dividend = 8
Divisor = 5
By solving the fraction we obtain the following result:
Quotient = Dividend \div Divisor = 8 \div 5
Since 8 is not completely divisible by 5 therefore the residue of division is called the remainder. The division can be performed till a zero remainder is obtained. The long division process of the above fraction is shown below:
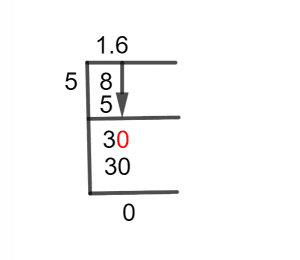 Figure 1
Figure 1
1 3/5 Long Division Method
The fraction is given as:
8 $\div$ 5
In division, we need a decimal point when the divisor is greater than the dividend and it is done by multiplying the dividend by 10. But in this case, we can see that 8 which is the dividend is greater than divisor 3, so in the first step, there is no need to multiply by 10.
8$\div$ 5 $\approx$ 1
Where:
5 x 1 = 5
And to find the remainder we have to subtract 8 – 5.
8 – 5 = 3
From the above division, the remainder obtained is 3. Further division is not possible without making the dividend bigger than the divisor. For this introduce a decimal point in the quotient and add zero with the remainder. Now the dividend is 30. Dividing it by 5 gives 6 with zero remainder
Here, 30 divided by 5 equals 6.
5 x 6 = 30
Because we currently have no leftover Remainders.
Thus, 30 – 30 = 0.
As a result, we conclude that the fraction 1 3/5 can be solved entirely and that the quotient has a value of 1.6 with no remainder.
Images/mathematical drawings are created with GeoGebra.
