What Is 20/40 as a Decimal + Solution With Free Steps
The fraction 20/40 as a decimal is equal to 0.5.
The Fractional result of a division of two numbers can be expressed into its equivalent decimal form using the long division method. In this process, the numerator is the dividend and the denominator is the divisor. The quotient found is the decimal value of the fraction and the remainder can or cannot be a non-zero value, depending on the fraction.
Here, we are more interested in the division types that result in a Decimal value, as this can be expressed as a Fraction. We see fractions as a way of showing two numbers having the operation of Division between them that result in a value that lies between two Integers.
Now, we introduce the method used to solve said fraction to decimal conversion, called Long Division, which we will discuss in detail moving forward. So, let’s go through the Solution of fraction 20/40.
Solution
First, we convert the fraction components, i.e., the numerator and the denominator, and transform them into the division constituents, i.e., the Dividend and the Divisor, respectively.
This can be seen done as follows:
Dividend = 20
Divisor = 40
Now, we introduce the most important quantity in our division process: the Quotient. The value represents the Solution to our division and can be expressed as having the following relationship with the Division constituents:
Quotient = Dividend $\div$ Divisor = 20 $\div$ 40
This is when we go through the Long Division solution to our problem. Given is the long division process in Figure 1:
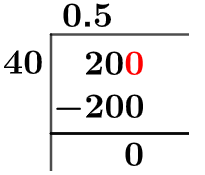
Figure 1
20/40 Long Division Method
We start solving a problem using the Long Division Method by first taking apart the division’s components and comparing them. As we have 20 and 40, we can see how 20 is Smaller than 40, and to solve this division, we require that 20 be Bigger than 40.
This is done by multiplying the dividend by 10 and checking whether it is bigger than the divisor or not. If so, we calculate the Multiple of the divisor closest to the dividend and subtract it from the Dividend. This produces the Remainder, which we then use as the dividend later.
Now, we begin solving for our dividend 20, which after getting multiplied by 10 becomes 200.
We take this 200 and divide it by 40; this can be seen done as follows:
200 $\div$ 40 $\approx$ 5
Where:
40 x 5 = 200
This will lead to the generation of a Remainder equal to 200 – 200 = 0.
Finally, we have a Quotient generated as 0.5, with a Remainder equal to 0.

Images/mathematical drawings are created with GeoGebra.
