What Is 3/10 as a Decimal + Solution With Free Steps
 The fraction 3/10 as a decimal is equal to 0.3.
The fraction 3/10 as a decimal is equal to 0.3.
The mathematical expression of something that is divided into equal parts or sections is called a Fraction. Components of a fraction are denoted by the Denominator, a number above the line or slash, and the Numerator, a number below the line or slash.
This slash indicates the process of Division. It might be tough to solve fractions using multiples other than those that correspond to their fractional representations however, converting them into division is a simple solution.
Therefore, instead of solving these fractions using the Multiples method, we use the Long Division method and get the results in decimal numbers.
Here, the fraction 3/10‘s decimal value is determined using the Long Division method.
Solution
To begin solving a fraction first, it has to be transformed into Division. It is the process of being divided or the act of dividing something into portions.
Initially, its elements are separated depending upon their function, which includes Dividend and Divisor. The Dividend designates the number that will be divided, whereas the term Divisor designates the number by which the dividend will be divided. In the fraction to solve, the dividend and divisor are 3 and 10, respectively.
After the division is complete, the result obtained is called the Quotient. Another term associated with division is Remainder which is the value left behind after partial division. When the divisor is not a dividend factor, the remainder is not zero.
In terms of dividend and divisor, 3/10 can be written as follows:
Dividend = 3
Divisor = 10
Quotient = Dividend $\div$ Divisor = 3 $\div$ 10
Here are specific directions for using the Long Division technique to resolve the fraction 3/10.
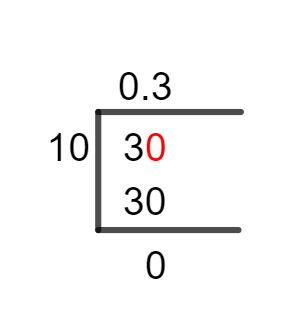
Figure 1
3/10 Long Division Method
The steps necessary to solve the fraction 3/10 are displayed below.
3 $\div$ 10
Identifying whether the dividend is bigger than the Divisor is the first step in long division. A Decimal Point must be added if the divisor is a larger number than the Dividend, by plugging in a zero to the dividend’s right. However, if the dividend is a greater number, we don’t need to use any decimal point.
In the above scenario, 3, the Divisor is less than 10, and the Dividend indicates that a Decimal Point is required to continue. So, we add a zero to the right of the 3 and make it 30 to have a decimal point in the Quotient.
Now calculations can be done as:
30 $\div$ 10 $\approx$ 3
Where:
10 x 3 = 30
To calculate Remainder, we can proceed as:
30 – 30 = 0
This division results in a Remainder of zero. It means that the fraction has been fully solved and that no additional computations are required and the Quotient, our precise and final outcome of this division, is 0.3.
Images/mathematical drawings are created with GeoGebra.
