JUMP TO TOPIC
Factors of 196: Prime Factorization, Methods, Tree, And Examples
The factors of 196 are those numbers that are entirely divisible by 196. As 196 is not a prime number, it has more than two factors that make the matter a little complicated, but all will be understood once you reach the examples section of this lesson.

Figure 1 – All possible Factors of 196
In this lesson, we will find multiple methods of calculating the factors of 196. Factors of a number are essentially those numbers that allow complete division of the given number.
What Are the Factors of 196?
The factors of 196 are the following: 1, 2, 4, 7, 14, 28, 49, 98, and 196. It has more than two factors because it is a composite number.
As it is a composite number, the factors it consists of are both prime numbers and composite numbers. These factors can also form pairs.
How To Calculate the Factors of 196?
The calculation of factors of 196 can be done using several methods such as the division method. Other methods are listed below:
- Division method
- Prime Factorization method
- Factor tree diagram
Among these methods, the division method gets the most attention because of its ease of use and simplicity. This method aims to find a number that gives a zero remainder on dividing with your original number; this divisor is your factor. Simple as that.
These methods operate on a similar foundation with minor differences that will be studied in the following article.
First, let’s take a look at the division method. The division of factors is given below:
\[ \frac{196}{1} = 196 \]
\[ \frac{196}{2} = 98 \]
\[ \frac{196}{4} = 49 \]
\[ \frac{196}{7} = 28 \]
\[ \frac{196}{14} = 14 \]
\[ \frac{196}{28} = 7 \]
\[ \frac{196}{49} = 4 \]
\[ \frac{196}{98} = 2 \]
\[ \frac{196}{196} = 1\]
Factors of 196: 1, 2, 4, 7, 14, 28, 49, 98, and 196.
Factors of 196 by Prime Factorization
The prime factorization method is a derivative of the basic division method but with the added conditionality of using only prime numbers for the division. The technique is basically about writing the original number as a multiplication of its prime factors.
The division proceeds until the answer can not be further divided and yields a resultant one.
The factors obtained through prime factorization have a unique disposition of producing the original number once they are multiplied by each other. This means that whenever the prime factors are multiplied, they will give the original number that was divided.
To understand this definition better, let us look at the mathematical representation of the prime factorization of 196:
196 can be divided into 2 and 98 (2 is prime, but 98 is composite):
196 $\div$ 2 = 98
98 is a composite number which is further divided into 2 and 49 (49 is a composite):
98 $\div$ 2 = 49
49 is further divided into 7 and 7, which are both prime numbers:
49 $\div$ 7 = 7
7 $\div$ 7 = 1
This is called prime factorization; the prime factorization can be represented in an equation as follows:
Prime Factorization of 196 = 2 x 2 x 7 x 7
OR
Prime Factorization = $2^{2}$ x $7^{2}$
The prime factorization of 196 is also shown below:
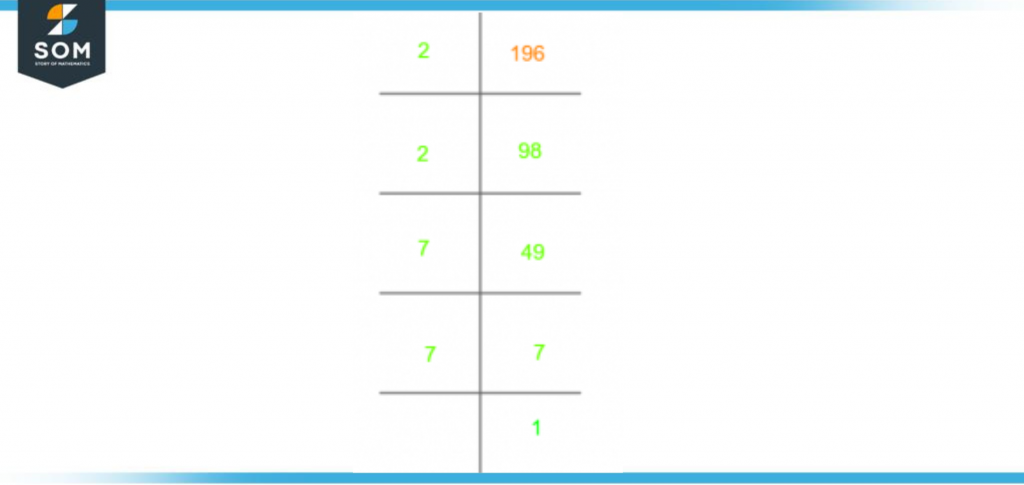
Figure 2 – Prime Factorization of 196
Factor Tree of 196
The factor tree of 196 is a visual diagram to understand and identify the prime factors of 196. This tool allows the user to calculate the prime factors simplistically, making it easier to understand.
At the head of the tree sits the original number 196. Upon each division, the tree divides into two branches.
The division is done in a way that at least one of the factors is a prime number; the division then continues from the composite number present in the branch. The division continues as long as there is at least one composite number in the tree.
The factor tree is represented intuitively in the shape of an actual tree branching out into only two divisions. Once all the branches end up with prime numbers, that is the cue to stop further division. All numbers present at the end or tips of the branches are called prime factors of the number, and we can not divide any further.
If we draw the factor tree of 196, we will see branches extending from the number, which will continue to extend and divide till all prime numbers are reached. This diagram is shown below in figure 3:
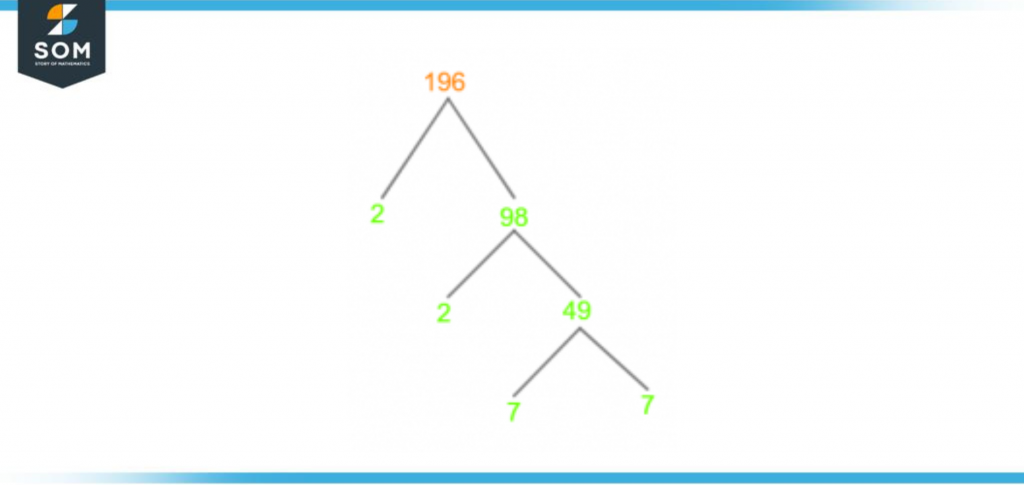
Figure 3 – Factor Tree of 196
Factors of 196 in Pairs
Factor pairs of a number are all the factors of this specific number that give the original number upon multiplication. This property is unique to factors and is quite amazing, given how both the positive and negative factor pairs yield the same answer.
The only condition necessary for any pair of factors to make a factor pair is the answer of their multiplication. If they give the given number upon multiplication, it is a factor pair; otherwise, they are just two random factors with no inherent mathematical significance.
As 196 is a composite number, it must have several multiples, but it is understood that 1 and 196 are its factors. Similarly, 1 and 196 make a factor pair because upon multiplication, they give the actual number: 196.
As all real integers can be positive or negative, it is fair to assume that the factor pairs will inherit the characteristics of real numbers as they are real too. Therefore, our number 196 will have not only positive factor pairs but also negative ones.
From earlier, we know that the factors of 196 are:
Factors of 196 = 1, 2, 4, 7, 14, 28, 49, 98, and 196
Any two random factors can not make a factor pair; they need to give the original number 196 upon multiplication; keeping that in mind, the positive factor pairs of 196 are:
Positive factor pairs of 196 = (1, 196), (2, 98), (4, 49), (7, 28), (14, 14)
This shows that 196 has a total of 5 positive factor pairs. To find the negative factor pairs, the solution is fairly straightforward, just add a negative (-) sign to all the numbers:
Negative Factor pairs of 196 = (-1, -196), (-2, -98), (-4, -49), (-7, -28), (-14, -14)
Factors of 196 Solved Examples
So far, we have learned quite extensively the concept of factorization and prime factors, so it is time that we apply our knowledge to the following example problems. This will allow us to tackle any question of relevant nature.
Example 1
Using the prime factorization method, find out the total factor of 196.
Solution
The prime factorization method is simpler to follow if one understands the concept of prime numbers; prime numbers are the numbers that are only divisible by 1 and the number itself.
In prime factorization, we calculate the prime factors of any number so that the prime factors will be all the factors of 196, but they must be prime numbers.
The prime factorization of 196 is given as:
In the first step, we need to divide 196 by 2:
196 $\div$ 2 = 98
We can see that 98 is an even number and divisible by 2, so we divide again:
98 $\div$ 2 = 49
49 is not an even number, so it is not divisible by 2, nor by 3, 5, which are the next prime numbers in line; in fact, it is a perfect square of 7, so we divide it by 7:
49 $\div$ 7 = 7
7 is a prime number and only divisible by itself, so we divide 7 by 7:
7 $\div$ 7 = 1
The factorization method ends when 1 is achieved, so our solution ends here. Now, to determine the prime factors, let us look at the divisors. The divisors are 2, 2, 7, and 7. These are our prime factors as well. So through prime factorization, the factors of 196 are:
Prime factorization of 196 = 2 x 2 x 7 x 7
The total number of prime factors are:
Prime factors of 196 = 2, 7
Example 2
Prove that 196 is not a prime number.
Solution
For any prime number, as we discussed earlier, it is imperative that it must not be divisible by any other number except one and the number itself. For example, 7 is a prime number because it gives a zero remainder upon division with 1 and 7 itself.
Similarly, 197 is a prime number because it is only utterly divisible by 197 itself and 1.
To prove that 196 is not a prime number, we need to show that it has multiple factors other than 196 and 1. To do that, we need to revisit the factors of 196. The total factors of 196 according to the division method are:
Total factors of 196 according to division method = 1, 2, 4, 7, 14, 28, 49, 98, and 196.
This shows that there are more than two factors of 196. It has a total of nine factors calculated through the division method. As there are several factors, this proves that 196 is not a prime number. Instead, it is a composite number that has multiple factors.
Hence, it is proven that 196 is not a prime number.
Example 3
Separate the even and odd factors of 196 and 25.
Solution
To separate the even and odd factors of 196 and 25, it is important that we first identify their factors, respectively. Then it will be easier for us to differentiate between them. Their factors are given below:
To calculate the sum of all the factors of 196 and 49, let’s first list down all these factors. These are given below; for ease of solution, both are:
Factors of 196 = 1, 2, 4, 7, 14, 28, 49, 98, and 196
Factors of 25 = 1, 5, 25
Now that we have their factors, we can separate them accordingly. Let us first separate the factors of 196 into even and odd. The even factors of 196 are given as:
Even factors of 196 = 2, 4, 14, 28, 98, 196
Odd factors of 196 = 1, 7, 49
Now we separate the even and odd factors of 25:
No even factors
Odd factors of 25 = 1, 5, 25
All images/mathematical drawings are created with GeoGebra.
