JUMP TO TOPIC
Factors of 53: Prime Factorization, Methods, Tree, and Examples
Factors of 53 are the numbers that divide 53 ultimately without producing a remainder. A number is regarded as a factor if it divides 53 and leaves a 0 as the remainder.
Figure 1 – All possible Factors of 53
What Are the Factors of 53?
The Factors of 53 are 1 and 53. Additionally, we are aware that the true divisors of the number 53 are its factors.This means that 53 is a prime number as it has two factors in total. The factor pairs of 53: (1, 53) and (53, 1). This can be done by pairing the numbers so that the final result is 53.How To Calculate the Factors of 53?
You can calculate the factors of 53 in two ways: Division and Multiplication. Put together a list of all the numbers that are less than or equal to the number whose factors you are looking for before calculating. Now in the case of 53, the numbers will be from 1 to 53.Thus, reducing each of them will give you the solution. It is noticeable that factors with odd numbers do not have two as one of their factors. There are multiple methods for calculating factors of integers.
The primary task in determining the factors through division is to compile a list of all the numbers lower than 53. Then multiply each number by 53. The divisions of 53 that leave a remainder of 0 are its factors. You will comprehend this idea better after going through the examples below:The number 53 can be divided using the lowest factor of all the numbers, 1. Therefore, 1 and 53 are the factors of the prime number 53.\[ \frac{53}{1} = 53 \] \[ \frac{53}{53} = 1 \] Accordingly, one can discover a number’s factors using division and multiplication. Finding integer factors can quickly be done using a variety of methods. The number is divided by itself until the remainder equals zero, at which point the quotient and the divisor are regarded as the factors of the specified number.Now, we will place more emphasis on multiplication to discover the factors of 53. Take figure 53 as the result of two whole numbers in all possible ways. Every integer found in any of these products is a factor of 53. The examples are shown below:1 x 53 = 53
53 x 1 = 53
So the factors of 53 are 1 and 53.Factors of 53 by Prime Factorization
The method of representing a number by a collection of factors multiplied together is known as Prime Factorization. It is a technique for determining or displaying a given integer as the sum of prime integers or in a different way.An answer is a decimal number when 53 is divided by numbers other than 1 and 53. To be the factors, the answer must be a whole number. This shows that they surely are not the factors of 53.Here are some examples:\[ \frac{53}{2} = 26.5 \] \[ \frac{53}{3} = 17.66 \]\[ \frac{53}{5} = 10.6 \]\[ \frac{53}{7} = 7.57 \]A prime number is made up of just the number itself and one. As a result, 53 is a prime number so it cannot be further factorized. Therefore, we conclude that 53 has a prime factorization of 53.53’s Prime Factorization is shown in the diagram below: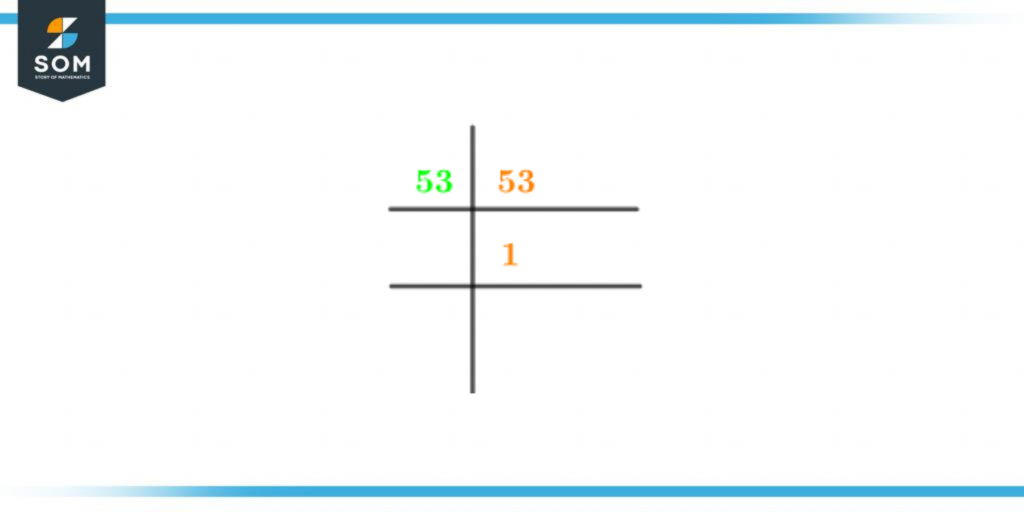
Figure 2 – Prime Factorization of 53
Factor Tree of 53
Finding the prime factors of any integer can be done using a factor tree. Finding a number’s factors is similar to tracing one’s family history. The number serves as the root of the factor tree, and until the prime number, all branches are factors.You can see the factor tree of 53 in the picture below: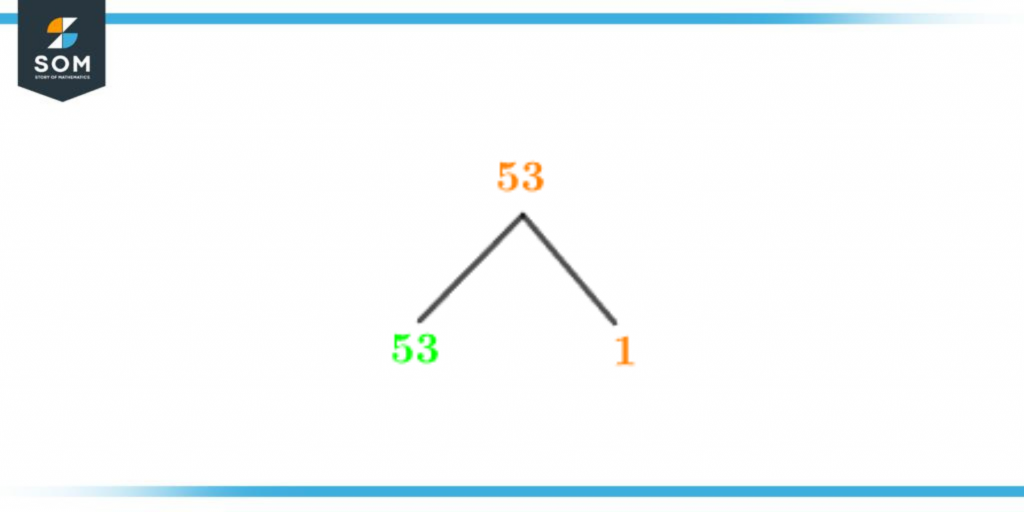
Figure 3 – Factor Tree of 53
- The sixteenth prime number is 53. Besides that, it is a Sophie Germain prime and an Eisenstein prime.
- Only a few other numbers share this trait with the sum of the first 53 primes: 5830, which is divisible by 53.
- In the periodic table, iodine’s atomic number is 53.
- Michael Jordan set an NBA playoff record in 1992 by making the most field goals in three-game series, which was 53.
- 53 is the largest possible National Football League team roster size.
- 53 is the number to reach Cuba with direct international dialing.
- Port numbers for the Domain Name System protocol are UDP and TCP.
- A book by Georges Perec is titled 53 Days, and the Northeastern American rock band is also known as 53 Days.
- Herbie, a fictitious Volkswagen Beetle with a mind of his own who made his film debut in 1968’s “The Love Bug,” had the race number 53.
- Wilt Chamberlain of Philadelphia scored the most points by a rookie in an NBA playoff game in 1960. It was 53.
- Many highways are numbered 53 worldwide, such as the Japan National Route 53 and N53 road in Ireland.
Factors of 53 in Pairs
Factor Pairs of 53 are any two numbers multiplied together to give 53. The following is a list of all the positive factor pairs of 53:1 x 53 = 53, (1, 53) is a positive pair factor of 53. 31 x 53 = 53, (53, 1) is a positive pair factor of 53. The fact that any two negative numbers can be multiplied together to produce a positive result makes negative pair factors possible. Simply switching the signs will bring to light the pair factors. The following list contains the pairs of negative factor pairs:-1 x -53 = 53, (-1, -53) is a negative pair factor of 53. -31 x -53 = 53, (-53, -1) is a negative pair factor of 53.Factors of 53 Solved Examples
Example 1
Anna is eager to purchase a puppy, but her parents are hesitant. The parents decided that if she answered their question correctly, they would buy her a cute puppy as she tried to persuade them daily. The question is “Determine the common factors of 53 and 106.” Find the correct answer to help Anna in purchasing a puppy.Solution
The factors of the prime number 53 are 1 and 53.The factors of the composite number 106 are 1, 2, 53, and 106.The common factors that lie between 53 and 106 are 1 and 53.Example 2
Ali’s mother instructed him to assist his younger brother with his math assignment. A list of factor pairs was given, and the first task on the math worksheet was to choose the factor pairs that make up 53.Here is the list of factor pairs:(2, 53) , (5, 53), (3, 5), (1, 53), (2, 26), (53, 1)
Identify the factor pairs of 53.Solution
Those numbers which result in 53, when multiplied, are collectively known as factor pairs. As 53 is a prime number, it only has two factors: one and itself.53 x 1 = 53
1 x 53 = 53
So, this means that (1, 53) and (53, 1) are the factor pairs of 53.Example 3
Sofia decided to purchase a pack of candies so that her 53 classmates may enjoy them while traveling as they would be going on a trip together. A pack of 53 candies was what she found. How many packs should she buy?Solution
There are 53 class fellows and 53 candies in total. Divide 53 by 53 to find the answer.\[ \frac{53}{53} = 1 \] Hence, Sofia should buy only one pack of candies.Example 4
Thomas has to deliver a package to Carnaby Street, but the problem is that he forgot the house number. On the package is a hint. The hint says, “ The house number is: Add all the factors of 53 to find out.”Solution
Here are the factors of 53: 1 and 5353 + 1 = 54
Therefore, Thomas has to deliver the package to house number 54, Carnaby Street.All the images/diagrams are made using GeoGebra.