JUMP TO TOPIC
Factors of 73: Prime Factorization, Methods, Tree, and Examples
A factor of 73 is supposed to be a number that divides 73 fully, without leaving any remainder behind. This number is supposed to be an integer, meaning it can be a positive or a negative number but cannot be in decimals or fractions.

Figure 1 – All possible Factors of 73
A straightforward approach to finding the factors of any number is to have basic knowledge of factors overall. One of the few things to know is that any number has a minimum of two factors. Such numbers are called prime numbers.
Methods for finding factors, prime factorization, factor tree, and factor tree will be discussed further in this article. Keep the basic knowledge in your mind while studying further; by the end, you can perform these methods for any number without being mistaken!
What Are the Factors of 73?
The factors of 73 are 1 and 73. These numbers are identified as the factors of 73, which means that when 73 is divided by both of these numbers, the answer is in whole numbers.
No other number could produce the same quotient for the number 73. As 73 only has two factors, it will be determined as a prime number.
How To Calculate the Factors of 73?
You can calculate the factors of 73 by determining the numbers that are exactly divisible by 73, using the multiplication and division methods. This means completing successful work for any number will help you identify two factors. These methods are multiplication and division.
We will consider numbers from 1 to half of that specific number for both methods. Any factor, other than the number itself, cannot be more significant than half of that number. This trick is shared for you to save your time and effort while working.
For division, we will find out half of that number. Then we will divide the given number by smaller numbers first. Once any number can generate a whole number as its answer, we have achieved our goal. Both the divisor and the quotient will now be considered as the factors of that number. That is how we retrieve two factors from one successful work.
We will calculate its half first to find the factors of 73 through division.
\[ \frac{73}{2} = 36.5 \]
Now 36 will be the largest number to be considered. One by one, all the numbers, from 1 to 36, will divide into 73. Any number dividing it entirely will be regarded as a factor of 73, along with the quotient. Since 73 is a prime number, only one will be able to divide it fully.
\[ \frac{73}{1} = 73 \]
For the multiplication procedure, different sets of two other numbers (smaller than or equal to the half) will be multiplied together, and the numbers that multiply to give the given number as the final product will be considered factors of that number.
One will always be multiplied by the number to get the essential pair as the answer. For the factors of 73 through multiplication, all the numbers from 1 to 36 will be considered.
Different pairs will be made to see which pair answers 73. Once finalized, both the numbers will be considered as the factors of that number.
Since it is a prime number, only one pair will give us our desired answer.
73 x 1 = 73
So both 1 and 73 are considered factors of themselves.
Factors of 73 by Prime Factorization
Prime factorization is a method to determine which prime numbers are the factors for the given number. When a prime number turns out to be a factor of any number, it will be called a prime factor.
Prime numbers are the only numbers beside the one which can divide them fully. So one and the number are considered factors of any number in general. Other numbers with more than two factors are called composite numbers.
So prime factorization can be called a decomposition method as it decomposes a certain number into its prime factors. This method starts by dividing the given number by the smallest divisible number. If the quotient calculated turns out to be a prime number, you will check the divisor.
As mentioned earlier, any number which divides a given number fully will be the factor of that given number. In contrast, the number divided by the smaller number will be known as the multiple of that smaller number. So we can say that every number is a factor and multiple of itself.
If it is a prime number as well, your answers are achieved, but if any one of the divisors and the quotient is a composite number, you will divide it further until both of your solutions are reduced to prime numbers.
A trick here is to know if the given number is a prime number or not beforehand. You will know this if you have already calculated the factors for that number earlier. Suppose it is a prime number. You must divide the number by 1 to get both prime factors.
For prime factorizing 73, we will start with the smallest divisible number. As we already know, it is a prime number, so that the smallest divisible number will be 1. After dividing it by 1, we will get 73 as our answer again. This indicates that it’s a prime factor in itself.
The representation of prime factorization looks similar to the method of LCM. An image of the prime factorization of 73 will be attached at the end of this article to help you understand the concept better.
The diagram of Prime Factorization can be seen below:
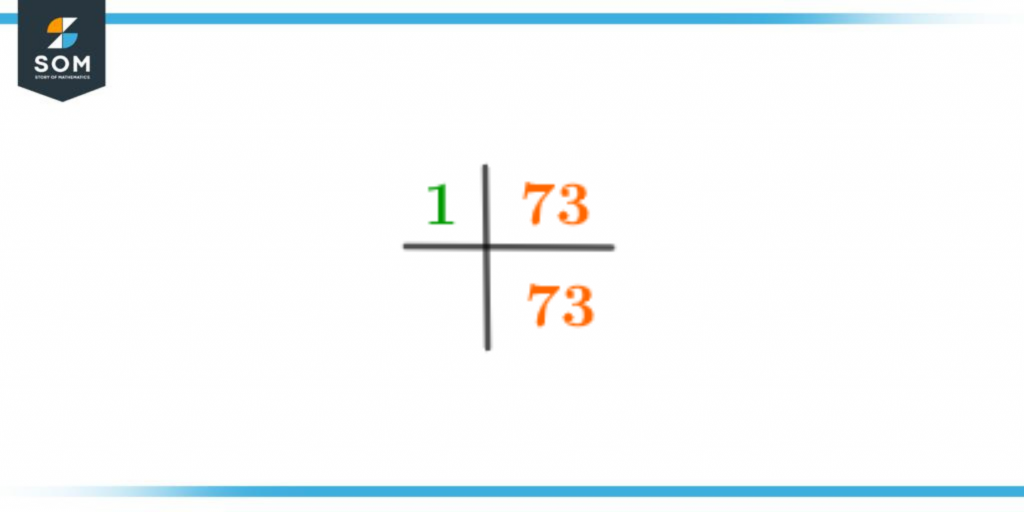
Figure 2 – Prime Factorization of 73
Factor Tree of 73
A factor tree is one of the ways of representing the prime factors for any number. This method can also describe the workings of any number’s prime factorization. It is a tool that breaks down a number into its prime factors.
The number for the work is written on the top. Then it’s divided by the smallest divisible number first (not 1). Then the divisor and the quotient will be written below the given number by emerging branches on either side of the number.
You will then check if any of both numbers is a composite number. If any of them is, break it down to its prime factors for the final results. The workings are the same as the prime factorization; only representation is different.
For the factor tree of 73, 73 will be written on top. Then you will divide it by its smallest divisible number, ‘1’. 73 will be the quotient. One will be noted on the right-hand side by extending a branch below, and 73 will be written on the other side similarly.
The factor tree of 73 can be seen on the diagram attached below:
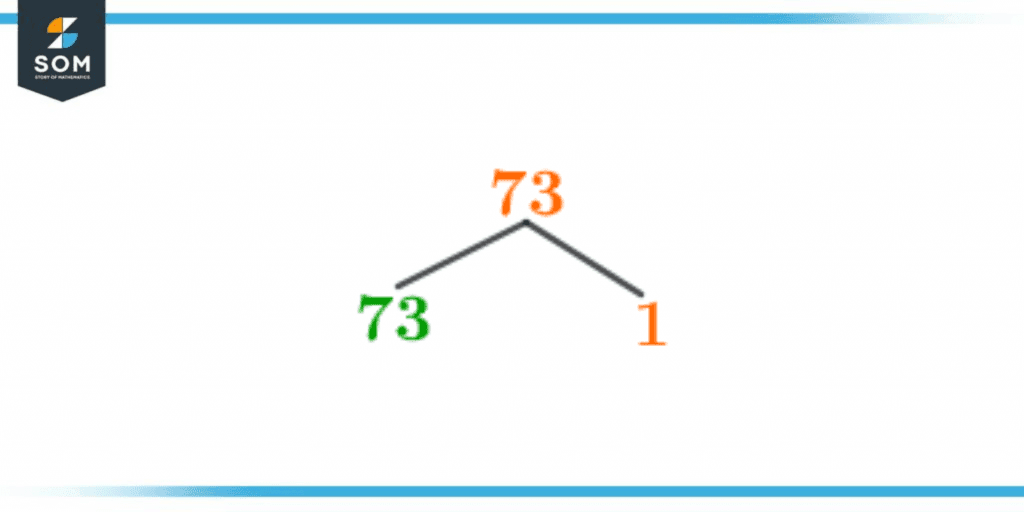
Figure 3 – Factor Tree of 73
Factor Pairs of 73
When two numbers multiply together to give a certain number as their final product, both these numbers together form a factor pair of that specific number.
We considered quotient and the divisor of one successful working as factors. Both of them together will form a factor pair for that specific number. The same is the case for the factors calculated through multiplication.
Factor pairs can be formed by negative numbers as well. A factor pair of any positive number in positive integers can create another factor pair for the same number just by changing the signs with the integers.
A prime number only has 1-factor pair. So the only factor pair of 73 is (1, 73). As discussed earlier, this pair can also turn into a pair with negative integers, giving us the same product when multiplied (-1,-73).
Factors of 73 Solved Examples
Example 1
Prove that (73, 1) is the factor pair of 73.
Solution
A factor of any number has to be smaller than or equal to that number. Any number larger than the given number cannot be the factor of that smaller given number.
\[ \frac{73}{1} = 73 \]
Upon dividing 73 by 1, we got 73 as the quotient. Quotient and divisor together form a factor pair of the dividend, so (73, 1) is a factor pair of 73.
Example 2
What are the negative factor pairs of 73?
Solution
The negative factor pair is given as follows:
(-1, -73)
All images/mathematical drawings are created using GeoGebra.
