What Is 2 4/5 as a Decimal + Solution With Free Steps
 The fraction 2 4/5 as a decimal is equal to 2.8.
The fraction 2 4/5 as a decimal is equal to 2.8.
A fraction is a completely special way of expressing a mathematical operation; it’s far equivalent to the Dot utilized in expressing a multiplication. A segment is commonly used to declare a division between two numbers that don’t resolve into an integer.
A fraction 2 4/5 is a mixed fraction. A mixed fraction is created when an improper fraction and a whole number are merged.
As we recognize that this kind of division is expressed as a fraction, and doesn’t produce an Integer, we come to locate that this division produces a Decimal value. A Decimal wide variety is exceptionally known as one which has two components, an entire number part, and a Decimal part. And it lies among Integers.
So, we can clear up the fraction given to us as 2 4/5 using the technique for fixing this kind of division, the long division method.
Solution
First, we convert the given mixed fraction 2 4/5 into a simple improper fraction which is done by multiplying denominator 5 with the whole number 2 and then adding the nominator 4 which is equal to 14/5.
\[ 2 + \frac{4}{5} = \frac{14}{5}\]
Now that we have converted the specified complete fraction into a division, we can begin to solve a fraction into a division. As we are aware, the numerator is equal to the Dividend, and the denominator is equal to the Divisor. We, therefore, define our Fraction as follows:
Dividend = 14
Divisor = 5
Now that we’ve examined the division of this fraction 5/14 and we call it Quotient i.e., the solution of this division.
Quotient=Dividend $\div$ Divisor = 14 $\div$ 5
Now by using the long division method we solve this problem:
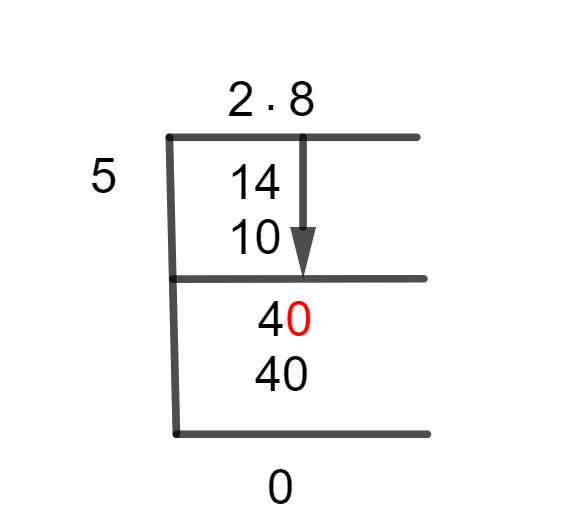
Figure 1
2 4/5 Long Division Method
We require a decimal point whenever the dividend is less than the divisor, which we can get by multiplying the dividend by 10. Therefore, we don’t require any decimal points if the divisor is smaller. Consequently, 14/5 is divided as follows.
14 $\div$ 5 $\approx$ 2
Where, 5 x 2 = 10
This demonstrates that there was also a remainder produced by this division, which is equivalent to 14 – 10= 4.
Next up, we examine our dividend 4 is smaller than divisor 5, so we must make it larger than the Divisor. We already recognize that below such instances we use the first rule of long division and multiply the dividend using 10.
However this additionally provides a decimal factor inside the Quotient, and this means we have obtained a quotient with 0 entire variety and no Decimal number. The Dividend, as a result, will become 40 and the solution is:
40 $\div$ 5 = 8
Where, 5 x 8 = 40
As a result, there is no remainder produced, and a Quotient with a value of 2.8 is achieved.
Images/mathematical drawings are created with GeoGebra.
