What Is 4 2/5 as a Decimal + Solution With Free Steps
 The fraction 4 2/5 as a decimal is equal to 4.4.
The fraction 4 2/5 as a decimal is equal to 4.4.
A fraction tells us the number of parts that make up the whole. The slash that is inserted between the two numbers identifies a fraction. The numerator is the upper part, and the denominator is the lower part.
A fraction appears in the numerator or denominator of a complex fraction. The numerator of a proper fraction is less than the denominator. It is known as an improper fraction if the numerator is bigger and can also be expressed as a mixed number, which is a whole-number quotient with a proper-fraction remainder.
By dividing the numerator by the denominator, any fraction can be expressed in decimal form. One or more digits may repeat indefinitely or the result may come to an end at some point.
We can use the long division method to solve the 4 2/5 fraction.
Solution
First of all, we convert the provided mixed fraction 4 2/5, into a simple improper fraction by multiplying the denominator 5 with the whole number 2 and then adding a nominator 2. This process yields the result which happens to be equal to 22/5.
\[ 4 + \frac{2}{5} = \frac{22}{5}\]
Now that we have converted the specified mixed fraction into an existing simple improper fraction, we can begin to solve an existing fraction into an existing division. As we have already developed the understanding that the numerator happens to be equal to the dividend, and similarly, the denominator happens to be equal to the divisor. We, therefore, define our fraction as follows:
Dividend = 22
Divisor = 5
Now that we have looked at the division of this fraction 22/5, we have named the result of this division the quotient.
Quotient=Dividend $\div$ Divisor = 22 $\div$ 5
Now, we may find a solution by applying the long division method:
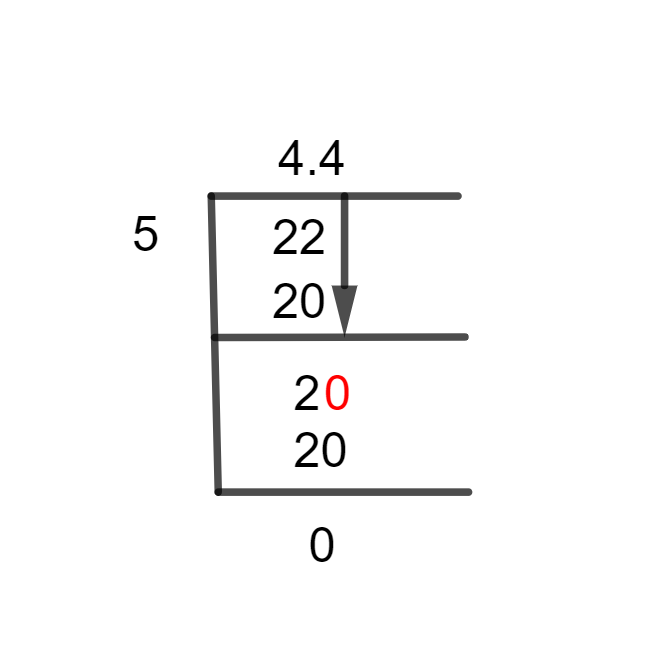
Figure 1
4 2/5 Long Division Method
We have:
22 $\div$ 5
When the dividend is smaller than the divisor, we need to add a decimal point, which we may do by multiplying the dividend by 10. Therefore, if the divisor is lower, we don’t need any decimal points. Thus, 22/5 is divided as shown below.
22 $\div$ 5 $\approx$ 4
Where, 5 x 4 = 20
This shows that this division also resulted in a remainder, which is equal to 22 – 20 = 2.
Next up, we will review our dividend 2 and if it is less than divisor 5, we must increase it. We already know that in these situations, we multiply the dividend by 10 using the first rule of long division.
We now have a quotient with 0 complete types and no decimal number, but this also introduces a decimal element into the quotient. As a result, the Dividend will increase to 20, and the solution is:
20 $\div$ 5 = 4
Where, 5 x 4 = 20
As a result, there is no remainder left, and a 4.4 quotient is obtained.
Images/mathematical drawings are created with GeoGebra.
