What Is 2/5 as a Decimal + Solution With Free Steps
 The fraction 2/5 as a decimal is equal to 0.4.
The fraction 2/5 as a decimal is equal to 0.4.
Fractions are used in mathematics to express two numbers having the operation of Division acting between them. But fractions are only valid for a number that cannot be solved down to an Integer using division. This is because when we cannot solve a fraction down to an integer, it results in a Decimal Number.
Now, solving a given fraction into a Decimal Number is a challenging task, compared to the standard division which solves completely. But there is a method that makes it easy, and it is called Long Division.
We will go through the solution of our fraction using the Long Division Method.
Solution
The first step toward solving this fraction into a Decimal Value is to convert this fraction into a division. For that, we transform its numerator into the Dividend and the denominator into the Divisor. This is therefore done here:
Dividend = 2
Divisor = 5
Now, we will also talk about the Quotient which represents the division’s solution. And to find the Quotient to this fraction turned into a division, we will have to use the Long Division Method.
Therefore, the Quotient is expressed as:
Quotient = Dividend $\div$ Divisor = 2 $\div$ 5
Without further ado, this is the Long Division Solution to our division:
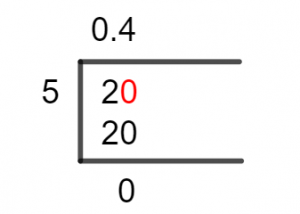
Figure 1
2/5 Long Division Method
This Method works by solving a division between two numbers in pieces, the pieces that we use may be generated by the problem itself. So, when solving a division by Long Division Method, we know that it cannot be solved using the Multiple Method.
Hence, we find the closest Multiple of the divisor to the dividend and subtract it from the dividend. The result which is also known as the Remainder dictates whether we carry on or not. If the result is not Zero, then we repeat the process on the value generated i.e., the Remainder.
And finally, when the dividend becomes smaller than the divisor, we use the decimal to multiply 10 by the dividend and then solve for that.
So, as our dividend is equal to 2 which is smaller than the divisor 5, the fraction is proper. This means that the Quotient is going to have 0 as the whole number, and a decimal point after that.
So, we will multiply the dividend by 10 and this produces the new dividend to be equal to 20. Now, let’s solve for 20/5:
20 $\div$ 5 = 4
Where:
5 x 4 = 20
Thus, we have no Remainder generated from this division, the divisor 4 is a factor of the new dividend 20. Now, the Quotient is going to be the combination of both zero and decimal points from the 10 multiplication, and the solution from this division.
Therefore, we have a Quotient equal to 0.4 with no Remainder.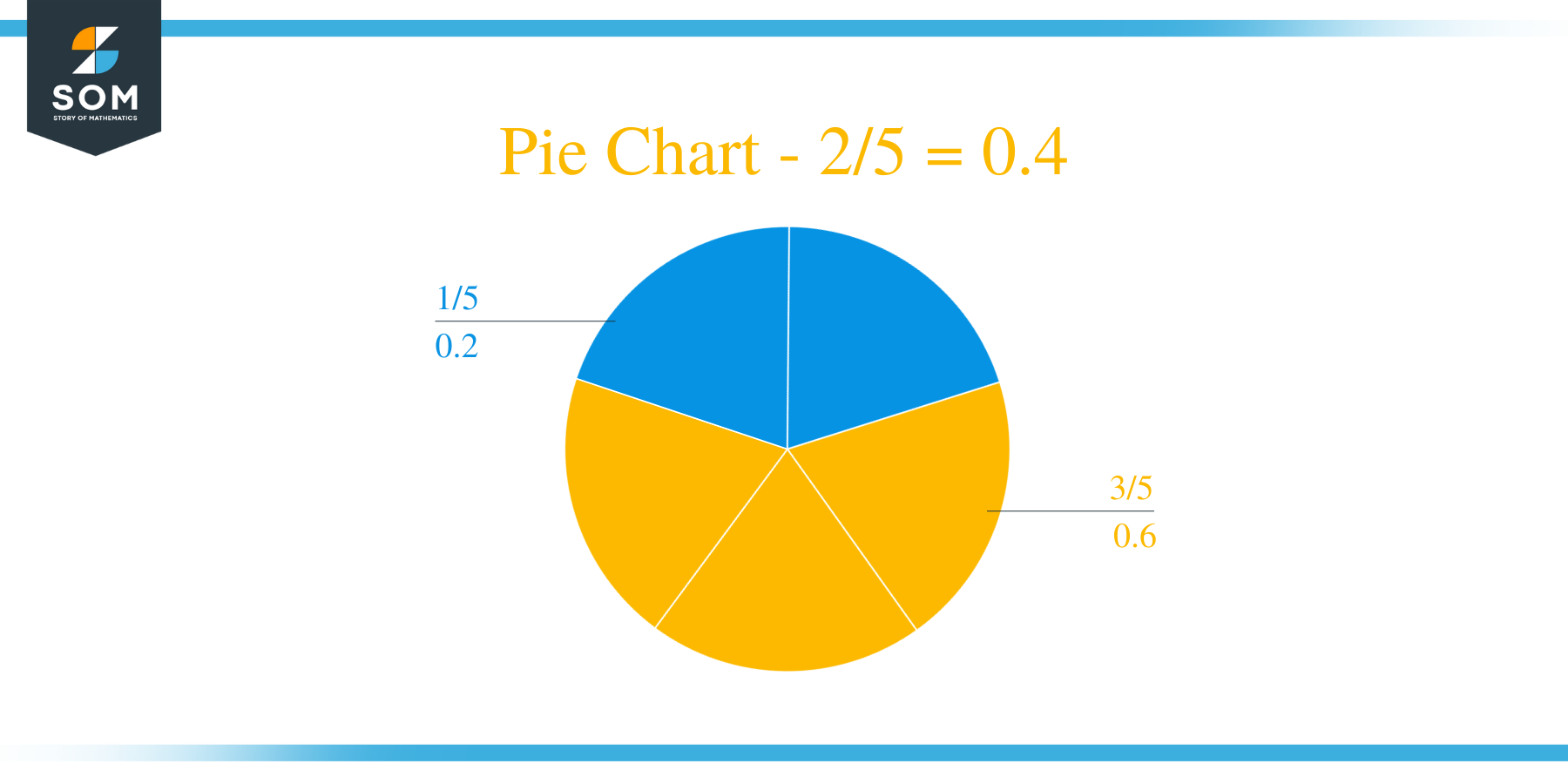
Images/mathematical drawings are created with GeoGebra.
