What Is 5/2 as a Decimal + Solution With Free Steps
 The fraction 5/2 as a decimal is equal to 2.5.
The fraction 5/2 as a decimal is equal to 2.5.
Fractions are used to express the mathematical operation of Division between two numbers. These numbers are when divided across each other, an incomplete complete division leads to a Decimal value as its result.
Now, to solve the operation of division when a number doesn’t completely divide across the other, we rely on a method called Long Division. Let’s look at the Long Division solution of the fraction 5/2.
Solution
We begin by getting the Constituents of a fraction set up. As we know, the numerator of a fraction is called a Dividend and the denominator is called the Divisor. Let’s make our fraction into a division.
Dividend = 5
Divisor = 2
Here, we will introduce the Quotient, which is defined as the solution of a division.
Quotient = Dividend $\div$ Divisor = 5 $\div$ 2
As we can see this fraction is now converted into a division and to find the Quotient, we must solve this division using the Long Division Method.
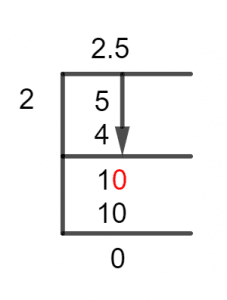
Figure 1
5/2 Long Division Method
Now, we start expressing our problem accordingly to fit the division criterion.
5 $\div$ 2
This expression of division can give a lot of information to us regarding the Quotient.
The Dividend and the Divisor have the specific impact that they make on the Quotient. And this is of the sort that if the dividend is smaller than the divisor the quotient is smaller than 1, and if the dividend is bigger than the divisor, the quotient is vice versa.
So, in our case, 5 is greater than 2 so our quotient would be larger than 1.
And finally, we come to the topic of Remainder. The Remainder as we already know is the remaining value from an inconclusive division, but it is a lot more than that. The remainder continuously becomes the new Dividend in our Long Division process.
Now, we can see that our dividend is bigger than the divisor, so we can solve it very easily.
5 $\div$ 2 $\approx$ 2
Where:
2 x 2 = 4
So, the remainder is equal to 5 – 4 = 1.
Now, we have the new Dividend equal to 1 because the remainder turns into the new dividend. We see that it is smaller than the divisor, so we introduce a Decimal point and get a zero for the dividend.
So, our new dividend is 10.
10 $\div$ 2 = 5
Where:
2 x 5 = 10
So, the remainder is equal to 10 – 10 = 0.
Hence, a Remainder of zero is produced. This means we did have a Conclusive division in this round. Now we have only one last thing to do. Connect both the non-decimal quotient part and the decimal quotient part.
This is very simply done here:
Non-decimal Quotient = 2
Decimal Quotient = 5
Quotient = 2.5
Images/mathematical drawings are created with GeoGebra.
