What Is 5/6 as a Decimal + Solution With Free Steps
 The fraction 5/6 as a decimal is equal to 0.83.
The fraction 5/6 as a decimal is equal to 0.83.
Fractions are a very common way of expressing when two numbers are associated with a division, but these are only used when the Division doesn’t end up in an integer. Thus, these fractions lead to the generation of Decimal Values.
A Decimal Number is composed of two parts, one is a Whole Number part which corresponds to the non-decimal number i.e., the one on the left of a decimal point. Whereas the other is the Decimal Part on the right of the decimal point.
To solve a fraction for its Decimal Value, we use a special method called Long Division. Now, let’s go through the solution for our division.
Solution
We kick off by first taking apart the Fraction which has been given to us i.e., $5/6$. There are two parts to this fraction $5$ is the Numerator, and $6$ is the Denominator. Now, as we transform this fraction into a division, we call $5$ the dividend, and $6$ the divisor. This is done as follows:
Dividend = 5
Divisor = 6
As we know that this fraction results in a solution, this solution for a division is referred to as a Quotient. The Quotient is dependent on the Dividend and the Divisor, and its value can be used to classify the kind of Fraction we are dealing with.
The Quotient’s relationship with the dividend and the divisor is expressed below:
\[Quotient=Dividend \div Divisor = 5 \div 6\]
Now, we shall solve this fraction using the Long Division method as follows:
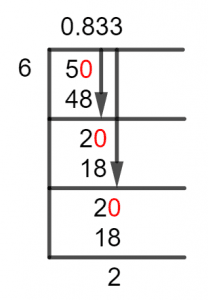
Figure 1
5/6 Long Division Method
To solve a division using the Long Division Method, we first understand how it works. The method solves problems involving dividends smaller than the divisors by Multiplying the dividend by $10$ and placing a decimal point in the Quotient.
Also, as the dividend is not a Multiple of the divisor, we find the closest multiple of the divisor to the dividend, and subtract it from the dividend, as that brings us the Remainder. The Remainder then becomes the new Dividend, and we solve for it until we find the solution up to the third decimal place.
Now, our dividend $5$ is smaller than the divisor $6$, so we place the decimal and get $50$ as our dividend, it may be noted that the Whole Number here would be $0$. So, let’s solve for $50/6$:
\[ 50 \div 6 \approx 8\]
\[ Where, \phantom {()} 6 \times 8 = 48 \]
This produces a Remainder of $50-48=2$, hence we repeat the process and get the dividend as $20$, solving for it goes as:
\[ 20 \div 6 \approx 3\]
\[ Where, \phantom {()} 6 \times 3 = 18 \]
Hence, a remainder of $20-18 = 2$ is produced again. If we look closely, we see that the Remainder is repeating itself, and so will the Quotient at this point. So, we conclude the division with the Quotient $0.833$ which has a repeating decimal number of 3.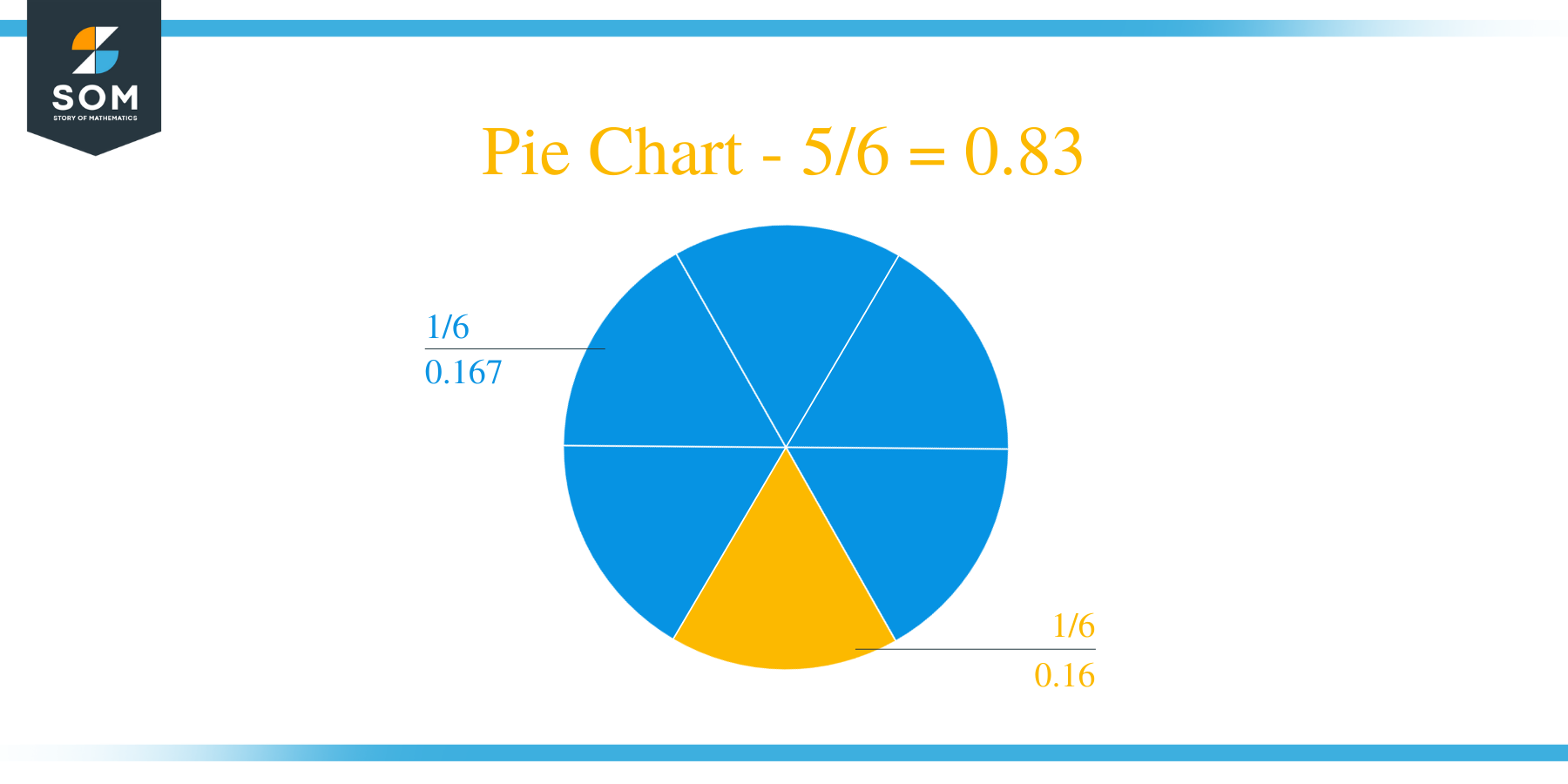
Images/mathematical drawings are created with GeoGebra.
