What Is 6 1/2 as a Decimal + Solution With Free Steps

The fraction 6 1/2 as a decimal is equal to 6.5.
Decimal Numbers are numerical values having a decimal point. A decimal point is present between its two parts, called the whole number and fractional parts. Such decimal numbers are primarily used in all types of calculations.
These numbers can be converted into Fractions by expressing them in the form of a ratio. For instance, a decimal number 0.2, when converted to a fraction, is described in the form of a ratio of 2/10.
Both fractions and decimals can be classified into different categories. The categories of fractions include Proper Fractions, Improper Fractions, and Mixed Fractions. This classification is based on comparing the numerator’s size and the fraction’s denominator. At the same time, classes of decimals are non–recurring or terminating decimals and recurring and non–terminating decimals.
Various methods are there to obtain a decimal value of a fraction. One is the Long Division method, which we will study in detail by converting a fraction of 6 1/2 into a decimal.
Solution
We are given a mixed fraction of 6 1/2 to solve. A mixed fraction is a fraction that has both a whole number and a fraction part. Thus, in 6 1/2, 6 is the fundamental number part, while 1/2 is the fractional part. To get its decimal value, we must start by converting it into an improper fraction.
The corresponding improper fraction of 6 1/2 is 13/2. Where 13 is the numerator, and 2 is the denominator. So, we need to divide 13 by 2. Thus, we have:
Dividend = 13
Divisor = 2
Two other terms related to the division are quotient and remainder. The Quotient is defined as the result of the process of the division, while the number left behind at the end of the operation is named the Remainder.
Quotient = Dividend $\div$ Divisor = 13 $\div$ 2
All steps of the Long Division of 13/2 are discussed here in detail.
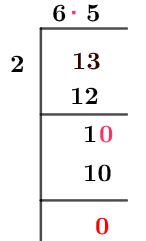
Figure 1
6 1/2 Long Division Method
We want to solve:
13 $\div$ 2
Since this fraction has 13 as a dividend and 2 as a divisor, which clearly shows that it is an improper fraction, a decimal point is not discoverable until it leaves a remainder smaller than the divisor.
Mathematically, this division is illustrated below.
13 $\div$ 2 \approx 7
2 x 6 = 12
We see that a remainder of 1 is produced.
13 – 12 = 1
We know the remainder is smaller than the divisor, so we now put a decimal point in the quotient and get 10 by multiplying the remainder 1 with 10. This 10 now acts as a dividend. The division steps are written below.
10 $\div$ 2 = 5
2 x 5 = 10
As 10 – 10 = 0, so we have 6.5 as this division’s Quotient or final decimal value.

Images/mathematical drawings are created with GeoGebra.
