What Is 6/11 as a Decimal + Solution With Free Steps

The fraction 6/11 as a decimal is equal to 0.545.
Decimal numbers are one of many different sorts of numbers. They are unique because they are formed from fractions. A decimal number is divided into two parts: the Whole Number part and the Decimal part.
A fraction has two parts, the Denominator and the Numerator. Usually, it is challenging to solve fractions using multiples other than their fractional representations, but converting them to Division is a simple solution.
Now, we will discuss the Long Division method for our fraction.
Solution
To begin, we take the dividend and divisor from our fraction. Considering that the numerator of a fraction is equal to the Dividend and the denominator is equal to the Divisor, In the fraction 6/11, the divisor is 6, and the dividend is 11.
We may deduce the following:
Dividend = 6
Divisor = 11
Two more division-specific concepts, quotient, and the remainder can now be used. As previously discussed, the division within a Fraction can be represented in great detail. For our fraction 6/11, we divide the number 6 into 11 pieces and then select one of those pieces as the value we seek.
It is also known as the Quotient, which is denoted as:
Quotient = Dividend $\div$ Divisor = 6 $\div$ 11
On the other hand, the term Remainder refers to a quantity left over following incomplete or partial division. Let’s look into the division’s Long Division Solution:
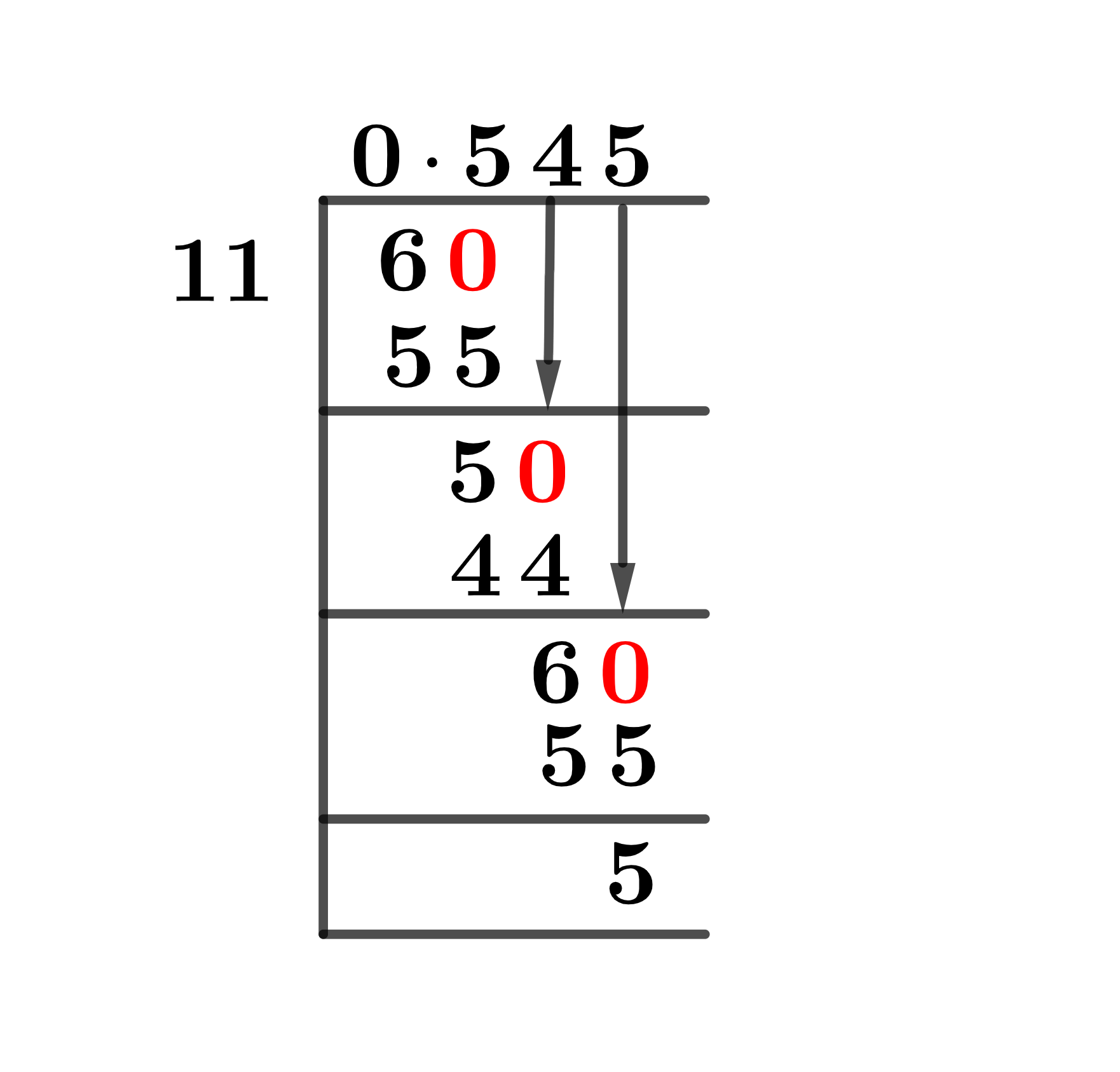 Figure 1
Figure 1
6/11 Long Division Method
The entire process for solving fraction 6/11 is described below.
6 $\div$ 11
When using the Long Division Method to divide a fraction, we must keep two things in mind. One, if the dividend is smaller than the divisor, we multiply it by 10 and enter the decimal in the Quotient. Second, we identify the divisor’s closest multiple to the dividend and deduct it from the dividend.
This subtraction produces a Remainder, which becomes the new dividend. So now we know our dividend 6 is less than 11. Let us use the decimal and make it 60. When you solve it, you get:
60 $\div$ 11 $\approx$ 5
Where:
11 x 5 = 55
The Remainder is as follows:
60 – 55 = 5
Because the Remainder has a non-zero value, we must solve it further to obtain complete results. As a result, we place a zero to the right of the Remainder but do not need a decimal point this time because Quotient already has a decimal value. The remainder is converted to 50. A further solution is as follows:
50 $\div$ 11$\approx$ 4
Where:
11 x 4 = 44
Reminder:
50 – 44 =6
It can be seen that this has produced our initial dividend again for us. We can do one more iteration for accuracy:
60 $\div$ 11$\approx$ 5
Where:
11 x 5 = 55
Due to the repetition of the remainders 5 and 6, the Quotient, which is 0.545, is a repeating decimal number.
Images/mathematical drawings are created with GeoGebra.
