What Is 7/8 as a Decimal + Solution With Free Steps
 The fraction 7/8 as a decimal is equal to 0.875.
The fraction 7/8 as a decimal is equal to 0.875.
The operation of Division between two numbers is not usually expressed widely, as it is done using a traditional method that uses Factors and Multiples. But, if a division cannot be solved using traditional factors and multiples, then we express them as Fractions.
A Fraction, therefore, plays a vital part in expressing a certain type of division, which can be solved. But first, they don’t result in Integers and second, they use a special method to be resolved into a solution. This method is called the Long Division Method.
We will look into the solution of our fraction 7/8 now and also dig deeper into the details of the Long Division Method.
Solution
To solve a fraction such as 7/8 to extract the Decimal Value from it, we rely heavily on the Long Division Method. And to begin solving this problem we first classify our fraction Components according to the division criterion.
So, the numerator becomes the Dividend, and the denominator becomes the Divisor. This is done as follows:
Dividend = 7
Divisor = 8
Now, we bring forth the quantity of Quotient, which describes the solution to a division problem. The quotient for our fraction to Division conversion, therefore, is given as follows:
Quotient = Dividend $\div$ Divisor = 7 $\div$ 8
The quotient is important as we are originally attempting to find its value, so now let’s find the quotient to this problem using Long Division:
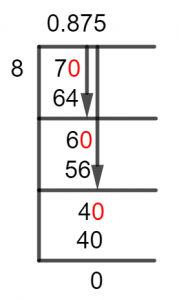
Figure 1
7/8 Long Division Method
Starting with the fraction 7/8, we begin to first analyze its nature, and we can see that it is a Proper Fraction, given the numerator is smaller than the denominator. Hence, when we solve this problem, we can find that its Quotient will be smaller than 1.
So, for a proper fraction, the Whole Number will be 0, and the decimal value would be found using the closest multiple methods.
Let’s analyze our dividend of 7, it needs to have a Zero to its right, and thus we introduce the Decimal Value. So, now having the dividend equal to 70 we begin to solve the following division:
70 $\div$ 8 $\approx$ 8
Where:
8 x 8 = 64
Hence, a remainder of 70-64 = 6 is produced, so we solve the next iteration using 6 as the dividend, and it produces:
60 $\div$ 8 $\approx$ 7
Where:
8 x 7 = 56
As we can see that this time a Remainder equal to 60 – 56 = 4 is produced, and we still don’t have a conclusive solution, so we repeat the process one last time for Accuracy. Hence, the Dividend becomes 40, and the solution is:
40 $\div$ 8 = 5
Where:
8 x 5 = 40
It turns out that we have found our solution with no Remainder generation, the remainder is therefore indeed zero. The dividend of 40 is a multiple of the divisor’s 8 and the Quotient generated is 0.875.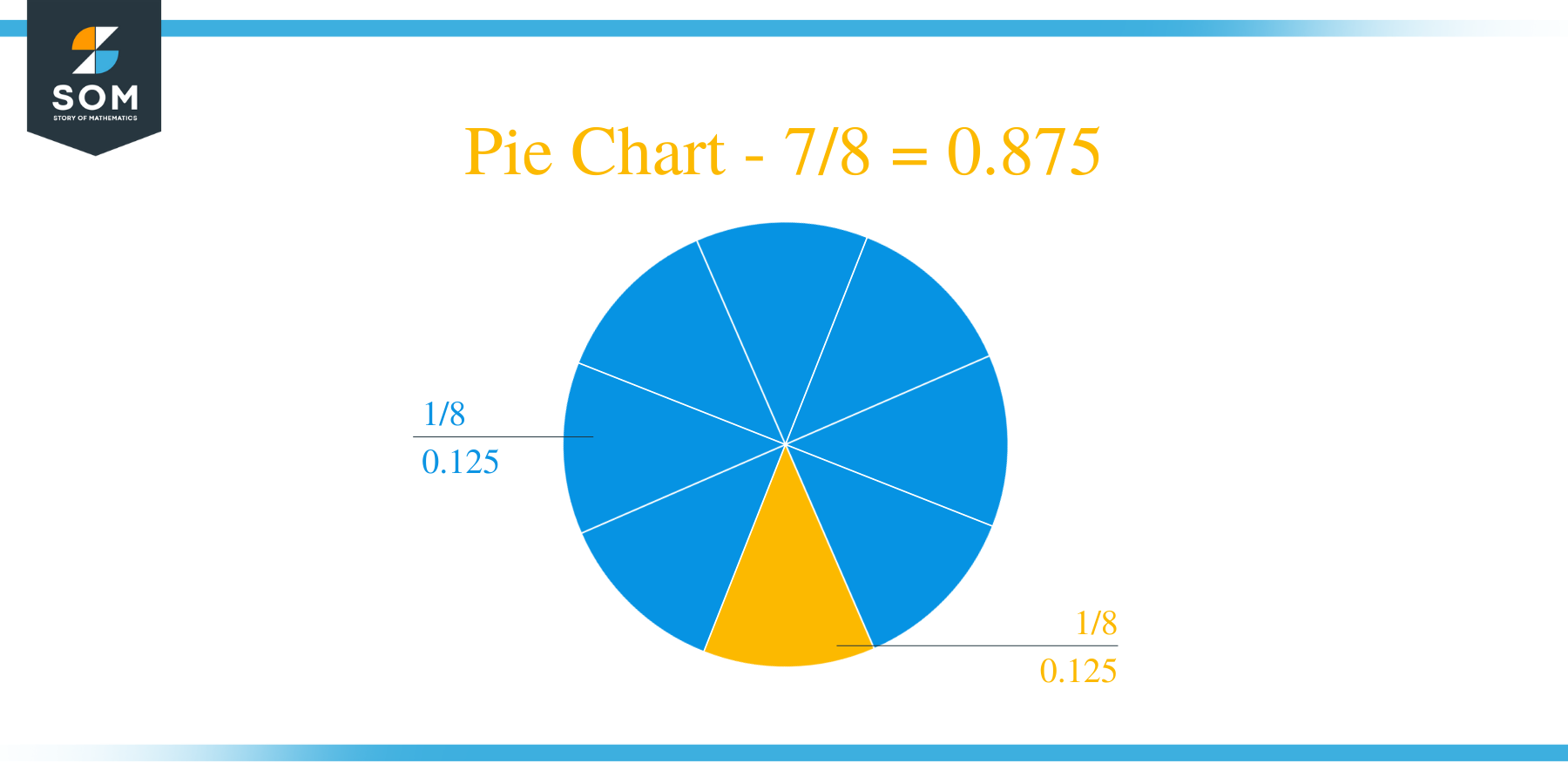
Images/mathematical drawings are created with GeoGebra.
