JUMP TO TOPIC
Model|Definition & Meaning
Definition
A mathematical model is something that describes the behavior of a system using mathematical language. A mathematical model is made up of a equation or group of equations that describe the dynamic behavior of the corresponding system and belong to a specific class of mathematical models.
A mathematical model is a system description that employs mathematical language and concepts. Mathematical modeling is the process of creating a mathematical model. Mathematical models are employed in the natural sciences, engineering, and non-physical processes, such as in the social sciences.
The Need for Mathematical Modeling
A Mathematics Model seems to be when we use math concepts and ideas to ‘model‘ a real-world object or situation. This can help us understand the real world and can be employed to improve many aspects of our lives. These models are vital to the working world, from safety to planning and construction.
More broadly, a model is a representation of an idea or object that is used to gain a better understanding of the real thing. A Model of a house, for instance, is used to demonstrate the design and layout of a real house before it is purchased or constructed.
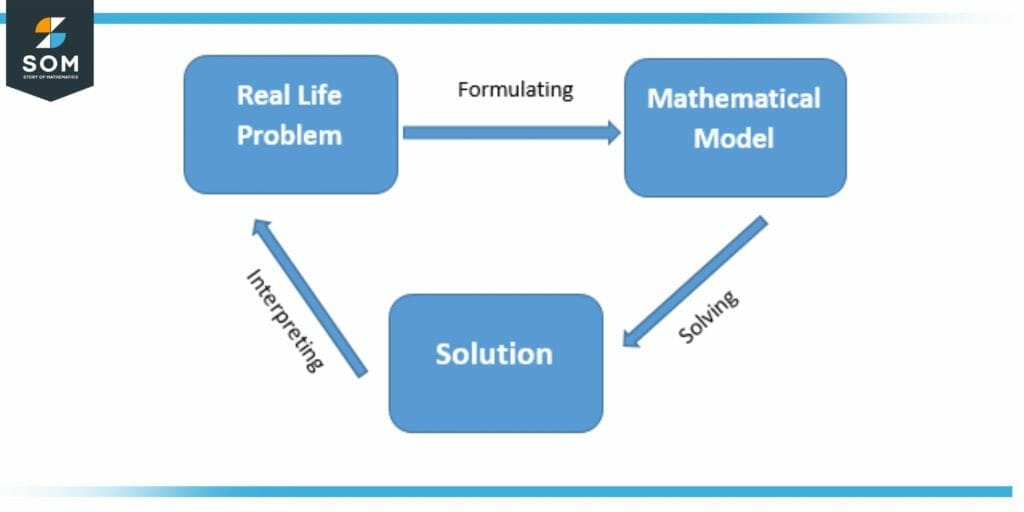
Figure 1 – Mathematical Modeling Flowchart
Estimated measurements are used in mathematical models to help us be more precise when planning what we can do with the real version of objects.
Checking the Precision of a Mathematical Model
Mathematical Models are representations of real-life objects, but they are not inherently perfectly accurate depictions of reality. We did not even consider other real-world factors in our examples, such as the cardboard’s size, the weight the box could hold, or if it would split apart when we used it to transport liquids. Most of these objects could be anticipated using more complex mathematical models, but remember that the model is only an estimate.
Some scientists use extremely accurate, complex models for critical tasks such as space exploration, which necessitates accurate estimation with little room for error.
However, for our applications, a simple model will be easier. The important question arrives here is determining whether that model is appropriate for the task at hand or not. If we are required to understand how many key components we might accommodate in the box, knowing the volume in the meter cube within that box would be incredibly helpful.
Classification of Models
On an implementation basis, we can categorize mathematical models into two main categories, which are further divided into two subcategories.
- Analytical
- Algorithmic
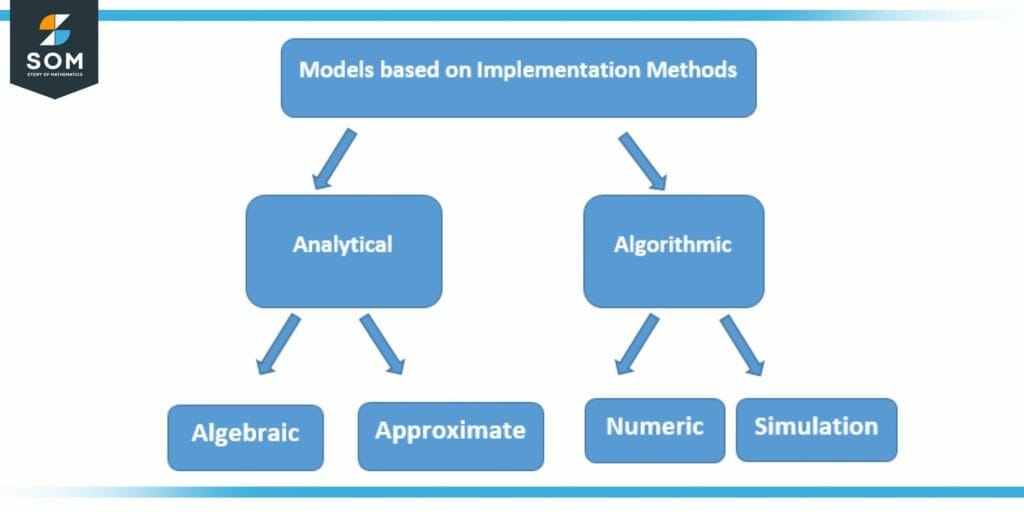
Figure 2 – Mathematical Models based on Implementation Methods
The two main categories, which are analytical and algorithmic, are further divided into two subcategories. Analytical has Algebraic and Approximation methods, whereas Algorithmic categories have Numeric and Simulation subdivisions.
Types of Mathematical Models
Mathematical models can be found all over the school levels. One of the most common types that we see in everyday life are equations, statistics, and graphs. The mathematical model for calculating any shape’s volume, area, or parameter is an equation.
The most commonly used mathematical model is an equation. Scientists like Albert Einstein used equations to build a sense of their surroundings. However, even young children in primary school will learn to use very basic equations, which will help them understand the concepts and factors behind their use.
Many mathematical models can be utilized to forecast what will occur in any given situation. Mathematical models, for example, are used to forecast the weather. This could tell you whether or not you should carry a coat to school.
However, it may also notify a business owner, such as an ice cream vendor, how many customers to expect in the park. It might even assist us in preparing for major storms.
Pie Chart
Mathematical models include pie charts, line graphs, and bar charts. They’re even used to discuss key points regarding large groups of statistics and numbers.
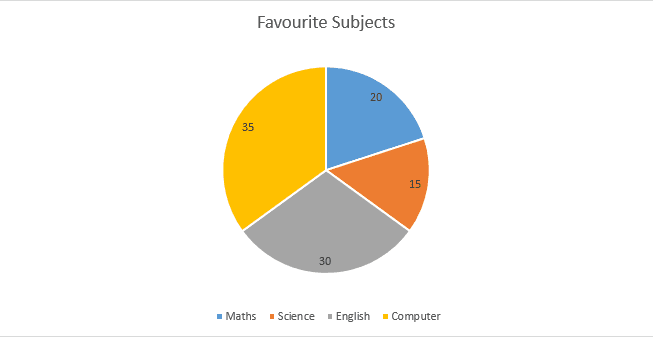
Figure 3 – Pie Chart of Favorite Subjects of the Students
The mathematical model above is a pie chart showing how many students like different subjects. Here, 35 students like Computer, 20 students like Maths, 15 Students like Science, and 30 students like English.
Line Graph
Here is another mathematical model of a line graph which shows the temperature of a city that changes with time during a whole day.
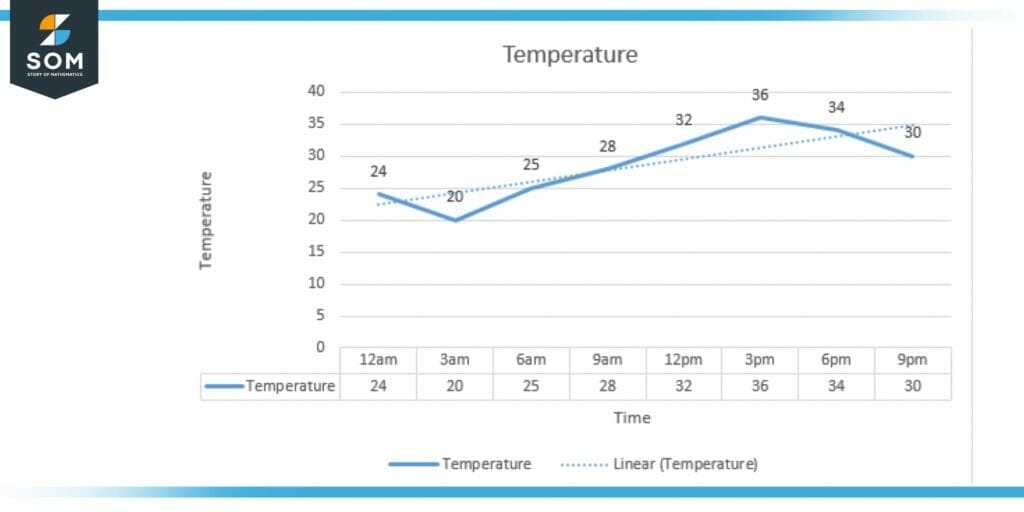
Figure 4 – Line Graph Model of Temperature with Time
The above model describes the temperature of a city that how temperature falls and rises with time. From this model, it becomes very easy for people to see the rise and fall of the temperature. So the mathematical model is very important in temperature prediction as well.
Equation
We just used a mathematical model that consisted equation or formula. But the common type of mathematical model is an equation.
Examples of Mathematical Modeling
Example 1
Jack plans to invest in some businesses that will return a profit of 20% per year. What will be the total money he gets at the end of the year?
Solution
Jack’s initial amount = x
Profit Jack gets per year = 20%
Total money Jack gets at the end of year = ?
Total money = x + (20%)x
20% = 20 ⁄100 = 0.2
Put the value of 20% in the above equation
Total money = x + 0.2x
Example 2
Solution
Length of field = 285 m
Cost to level the field = 20 cents per square meter
Area of square = side²
here length = side
Area of square = 285²
Area of square = 285 x 285
Area of square = 81225 m²
Cost to level the area = 20 x 81225
Cost to level the area = 1624500 cents
All the above figures are created in GeoGebra.
