What Is 11/12 as a Decimal + Solution With Free Steps
 The fraction 11/12 as a decimal is equal to 0.916.
The fraction 11/12 as a decimal is equal to 0.916.
A Fraction is regarded as a piece of something greater. It defines the equal components obtained from a whole quantity. A fraction is made up of two constituents, the numerator, and the denominator.
The top number is known as the Numerator, and the bottom number is known as the Denominator. The denominator represents all equally sized portions or parts, whereas the numerator represents the number of parts taken.
Long Division is used in this case to resolve the provided fraction of 11/12.
Solution
To solve a fraction, first, convert it into a division, and we know that a division contains dividends and divisors. As a result, the numerator 11 is now the Dividend, and the denominator 12 is the Divisor:
Dividend = 11
Divisor = 12
In mathematics, a quotient is defined as the result of dividing an integer by any divisor:
Quotient = Dividend $\div$ Divisor = 7 $\div$ 4
Another essential division term is Remainder, which is the value left behind after incomplete or partial division.
Let’s use the Long Division Method to solve our fraction:
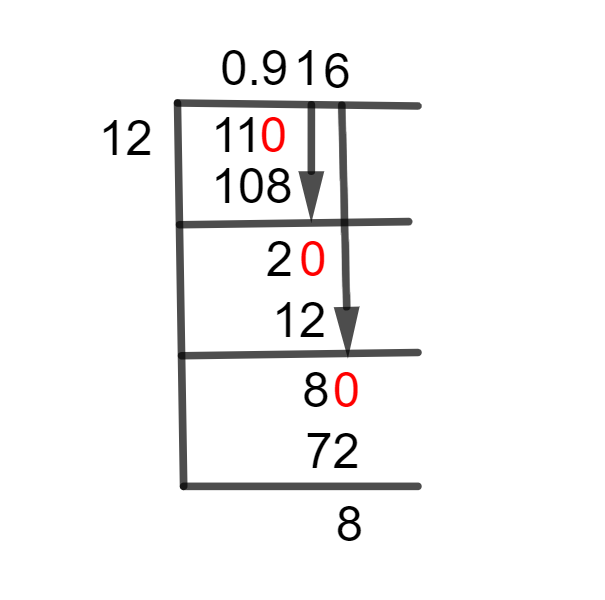
Figure 1
11/12 Long Division Method
We will go through the entire Long Division procedure to solve this fraction :
11 $\div$ 12
As we can see, a dividend is smaller than a divisor which means 11 is smaller than 12. To compute this provided fraction, we must have a Decimal Point. This is accomplished by inserting a zero to the right of the remainder. As a result, we receive 110, which must now be divided by 12. The division steps are outlined below:
110 $\div$ 12 $\approx$ 9
Where:
12 x 9 = 108
After this division, the remainder we are left with is:
110 – 108 = 2
If there is a remainder, we will repeat the method and multiply the dividend by another 10. It sets the dividend from 2 to 20. As a result of resolving this, we get:
20 $\div$ 12 $\approx$ 1
Where:
12 x 1 = 12
The remainder we are left with is:
20 – 12 = 8
Again we have remainder 8, which is smaller than the divisor, so we multiply it by 10 and make it 80 to continue over the solution:
80 $\div$ 12 $\approx$ 6
Where:
12 x 6 = 72
The remainder we have is:
80 – 72 = 8
As a non-zero remainder is formed, we add a zero to the right of the remainder, but this time the decimal point is unnecessary because we already have a quotient with the decimal value. We can also observe that the remainder has the same value as before, which is 8. As a result, the preceding processes will be repeated.
As a result, we can end our division here and state that this is a Repeating Decimal Number with 6 as the repeating number and 0.916 as the Quotient.
Images/mathematical drawings are created with GeoGebra
