What Is 11/20 as a Decimal + Solution With Free Steps
 The fraction 11/20 as a decimal is equal to 0.55.
The fraction 11/20 as a decimal is equal to 0.55.
A Fraction between two numbers describes a division occurring of one number across the other. Now, the Division here is of utmost importance as it describes the type of number which is going to be produced as its Result.
Now, there are two most general types of Division, complete and incomplete or inconclusive. A complete division would solve up to an integer, whereas an incomplete one would lead to a Decimal Value.
We are therefore interested in the inconclusive type of Division as it is the most common reason a Fraction is expressed as a fraction because it cannot be simplified anymore.
Now, let’s look at the solution for our fraction of 11/20.
Solution
We begin by first dividing our fraction into its components, i.e., the Dividend and the Divisor, the numerator, and the denominator respectively. This is important because we define an incomplete division as the absence of a Factor for the dividend in the denominator.
We express the fraction’s components as follows:
Dividend = 11
Divisor = 20
It is common knowledge that the solution of a division is referred to as the Quotient. The Quotient is directly dependent on both the Dividend and the Divisor for whatever value it takes up.
In general, a dividend smaller than the divisor would result in a Quotient smaller than 1 and vice versa.
Quotient = Dividend $\div$ Divisor = 11 $\div$ 20
We have talked a lot about the nature of this division, but now we must move forward to the Method used for solving said division. This is called Long Division, and the solution of our fraction 11 / 20 is given as follows:
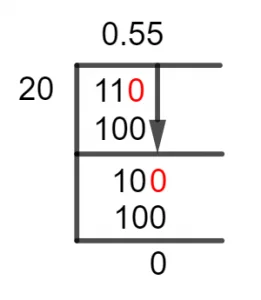
Figure 1
11/20 Long Division Method
We start by moving directly forward with the division operand instead of the fraction, as we begin with the Long Division Method:
11 $\div$ 20
Finally, we have one last value of significance, and it is the Remainder, the number which gets left behind after an incomplete division iteration. The most important fact about this is that it then becomes the new Dividend.
So, as the dividend is Smaller than the divisor, we begin by introducing a Zero into the dividend:
110 $\div$ 20 $\approx$ 5
Where:
20 x 5 = 100
Hence, the Remainder is 110 – 100 = 10.
We get a Remainder equal to 10, which is still smaller than 20 so we take another Zero and get the new dividend to be 100:
100 $\div$ 20 = 5
Where:
20 x 5 = 100
Hence, we have no remainder produced, the second iteration of the Long Division produced a complete division solution. Now, we just compile our values together:
11 $\div$ 20 = 0.55
The Quotient is therefore indeed 0.55 and is solved to completion.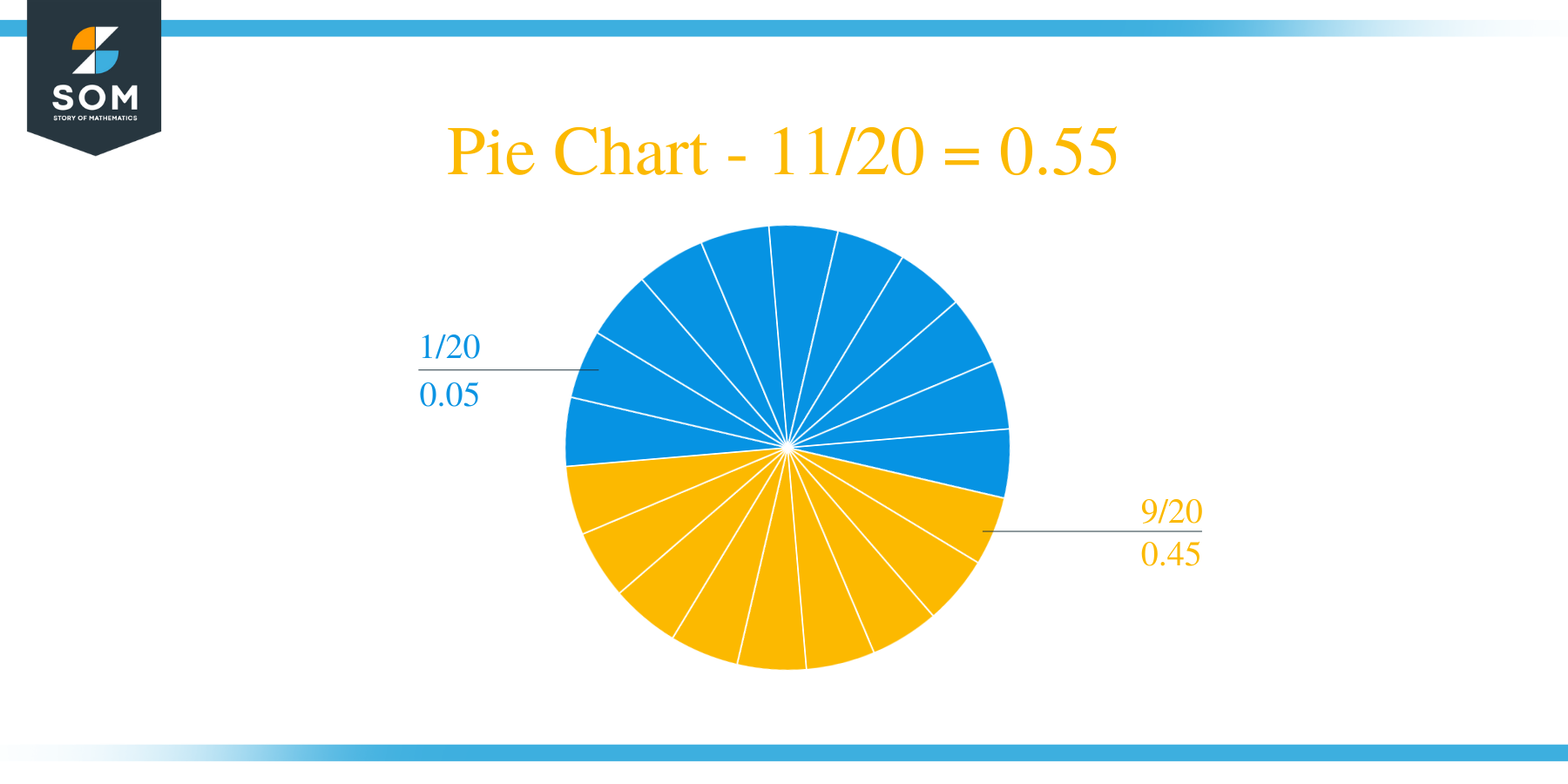
Images/mathematical drawings are created with GeoGebra.
