What Is 2/6 as a Decimal + Solution With Free Steps
 The fraction 2/6 as a decimal is equal to 0.333.
The fraction 2/6 as a decimal is equal to 0.333.
The mathematical operation of Division seems to be the most challenging of all the mathematical operations. However, there is a Technique to deal with this allegedly difficult problem, that makes it quite simple. The problem arises when dealing with Fractions, they represent numbers that are not integers.
Long Division Method is thus a method used for converting fractions that cannot be simplified into their corresponding decimal numbers.
So, we will delve deeper into the solution of this fraction using Long Division, which takes apart the fraction and solves it in several steps.
Solution
To start, we first classify the components of the Fraction according to how they function. In a fraction, the numerator is known as the Dividend. It is the number that needs to be divided.
Whereas the denominator is referred to as the Divisor. It is the number that divides the dividend. In this question, the Dividend is 2, while the Divisor is 6. It gives us the following result:
Dividend = 2
Divisor = 6
Moving forward, we rearrange this fraction to be more illustrative and introduce the terms Quotient and Remainder. Quotient refers to the result of a division, while Remainder refers to the remaining value obtained from an incomplete division.
Quotient = Dividend $\div$ Divisor = 2 $\div$ 6
Here we look at the Long Division Solution to our problem:
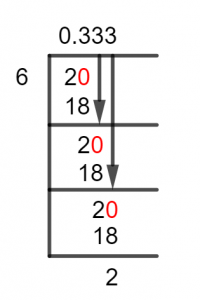
Figure 1
2/6 Long Division Method
In the question, we are given:
2 $\div$ 6
We can see that the dividend is a Factor of the divisor so, we can simply the division as:
1 $\div$ 3
So, moving forward with the Long Division, we first check whether the first digit of the Dividend is greater or smaller than Divisor. As we have a single digit in dividend 1 and it is smaller than divisor 3, it is not possible to divide this fraction without using a Decimal Point.
So, first, we insert a Zero to the right of the dividend, that is 1, and transform it into 10, to add the desired decimal point. Then, we calculate the Division Operation for these two numbers:
10 $\div$ 3 $\approx$ 3
Where:
3 x 3 = 9
We can see that a Remainder is produced as a result of this division and is equivalent to 10 – 9 = 1.
After generating a remainder, we go through the process again and add a zero to the right of the remainder. Since now the Quotient already has a decimal value, we don’t need to add another one.
Hence, we have:
10 $\div$ 3 $\approx$ 3
Where:
3 x 3 = 9
Solving it for the second time shows that the remainder produced keeps on Repeating and so will the Quotient. Thus, we have a Recurring Decimal Value on our hands here. Therefore, the resulting Quotient is 0.333 with a constant Remainder 1.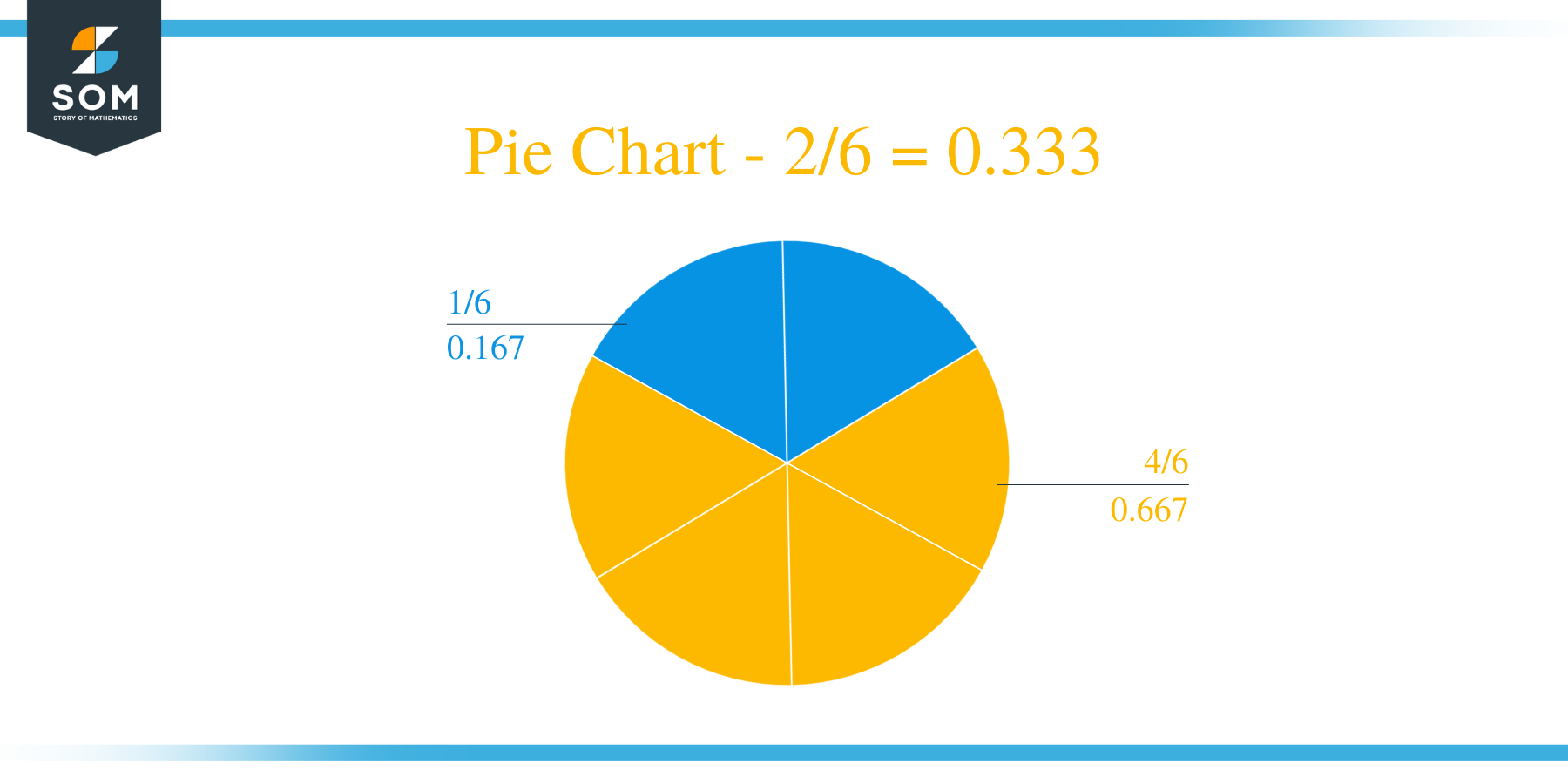
Images/mathematical drawings are created with GeoGebra.
