What is 13/20 as a Decimal + Solution with Free Steps
 The fraction 13/20 as a decimal is equal to 0.65.
The fraction 13/20 as a decimal is equal to 0.65.
A fraction is a very unique way to communicate a mathematical operation; it is comparable to using a dot to represent the result of a multiplication. Because of this, a fraction is typically used to indicate a division between two integers that doesn’t result in an integer.
Of all the mathematical operations, division appears to be the most challenging. But it doesn’t have to be that way because there is a solution to deal with this ostensibly challenging issue. Long Division is the technique in question for resolving fractions.
We will use long division to solve the given fraction, which is 13/20, as it will result in the decimal equivalent.
Solution
We start by first dividing the fraction’s components according to how they function. When a fraction is divided, the numerator is referred to as the Dividend and the denominator as the divisor. Now we can express this fraction in terms of division components as follows:
Dividend = 13
Divisor = 20
Here, we look at the Quotient which is defined as the result of a division. Now the relationship between the dividend and divisor can be tied together with the Quotient for our problem as follows:
Quotient = Dividend $\div$ Divisor = 13 $\div$ 20
Now, by utilizing long division, we may resolve the issue as follows:
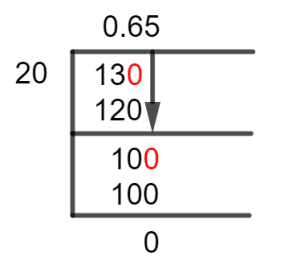
Figure 1
13/20 Long Division Method
You can take a closer look at the Long Division Method utilized to fix this issue by doing the following.
We had:
13 $\div$ 20
Since 20 is greater than 13, as we all know, you cannot divide this number without using a decimal point. This is because the divisor needs to be smaller than the dividend. We now insert a zero to the right of our remaining amount to add the desired decimal point.
The remainder is a different division-specific phrase for the value that remains after an incomplete division. We will add the Zero to its right, making the 13 in this scenario 130 because it is a remainder. Now, we determine:
130 $\div$ 20 $\approx$ 6
Where:
20 x 6 = 120
This indicates that a Remainder too was obtained from this division, and it is equivalent to 130 – 120 = 10.
We repeat the operation after obtaining a remainder from the division and add a zero to the remainder’s right. Given that the Quotient is already a decimal value in this scenario, we won’t need to add another one.
The remainder was 10, thus adding a zero to its right will result in a result of 100. We can now proceed and perform the calculation:
100 $\div$ 20 = 5
Where:
20 x 5 = 100
Thus, we see that our division has resulted in a solution that has no Remainder, and the dividend can be solved as the Multiple of the divisor. So, we have a Quotient that is equal to 0.65.
Images/mathematical drawings are created with GeoGebra.
