What Is 9/5 as a Decimal + Solution With Free Steps
 The fraction 9/5 as a decimal is equal to 1.8.
The fraction 9/5 as a decimal is equal to 1.8.
The fraction can be expressed in p/q form, where p is referred to as the Numerator, and q is referred to as the Denominator. The fraction can be solved by a division and it seems one of the most difficult mathematical operations but actually, it is not. There are simpler ways to solve this operator. One of the best and most prominent methods used to solve fractions is Long Division.
The step-by-step approach of the Long Division method is discussed in fraction 9/5.
Solution
Understanding terms is very important before solving any mathematical problem. Because by doing so, the problem and its solution become easier to elaborate on. the two terms that must be introduced before starting the problem are Dividend and Divisor. The number before the fraction sign is known as the Dividend and the number that arrives after the fraction part is referred to as Divisor. Or if we talk about the p/q form, p is referred to as the Dividend while q is the Divisor.
Dividend = 9
Divisor = 5
By solving a mathematical problem, we have a result in the end. In the case of solving fractions by using the long division method, the result is known as the Quotient.
Quotient = Dividend $\div$ Divisor = 9 $\div$ 5
Now, by using the Long Division, the problem can be solved as: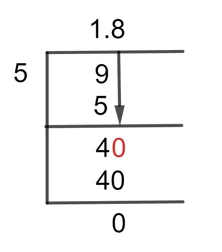
Figure 1
9/5 Long Division Method
The fraction 9/5 can be solved by Long Division through the method shown below.
So the fraction we have is:
9 $\div$ 5
If the numerator is greater than the denominator, then we can directly proceed with the solution, but if we have a numerator less than the denominator, then we have to add the Decimal Point first. But in the given fraction we have numerator 9, which is greater than the denominator so we can directly do the division process without adding decimal points.
Another term is required to be introduced before starting the solution, which is Remainder. As its name implies, it is the remaining part we get after the incomplete division in the long division method.
In this case, we have 9 as a numerator and we do not need to add a decimal point so the solution proceeds as follows:
9 $\div$ 5 $\approx$ 1
Where:
5 x 1 = 5
By doing so, we come up with the remainder of 4. Now remainder is less than the Divisor, so we will add the Decimal point to the Quotient. Now we can add the Zero to the Remainder’s right to further proceed with our problem. So the new remainder now is 40.
40 $\div$ 5 = 8
Where:
5 x 8 = 40
After this step, we now have the Remainder that is 0, which means now there is no need to solve the problem further and the resulting Quotient is 1.8 for the fraction 9/5.
Images/mathematical drawings are created with GeoGebra.
