What Is 7/16 as a Decimal + Solution With Free Steps
 The fraction 7/16 as a decimal is equal to 0.4375.
The fraction 7/16 as a decimal is equal to 0.4375.
A Fraction between two numbers doesn’t just correspond to a division occurring, it means that it can’t be solved further. This is because the division involved with a fraction is inconclusive, as it doesn’t result in an Integer Value. This is because such a fraction results in a Decimal Value.
Decimal Numbers are very intriguing as they are made up of two types of numbers, one is the integer which defines the closest fixed value known as the Whole Number. And the other is the decimal number, which is smaller than an integer, and thus is added on top of the referencing integer known as the Whole Number.
Now, the method used for converting a fraction into a decimal number is called Long Division. So, let’s go through our fraction’s solution.
Solution
The first step in solving this division is Converting the given fraction into a division. This is done by transforming the numerator into the Dividend and the denominator into the Divisor. It can be seen done here:
Dividend = 7
Divisor = 16
We understand that in the division, the dividend is Broken Down into a lot of pieces, and the number of those pieces is determined by the divisor. The divisor in our case is 16, so we are breaking 7 down into 16 pieces and one of those is described by the division.
This will thus result in the Quotient of our division, given as:
Quotient = Dividend $\div$ Divisor = 8 $\div$ 11
Now, we will go through the solution of our division using the Long Division Method:
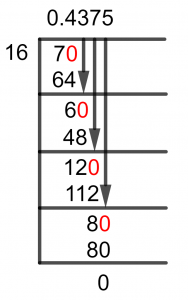
Figure 1
7/16 Long Division Method
So we start solving a division using the Long Division Method by first considering how it works. The first thing to keep in mind is to know that our divisor is not a Factor of the dividend, and hence we have to find the Closest Multiple to the dividend of the divisor.
That Multiple is then subtracted from the dividend, and that becomes the new dividend for the next division, also called the Remainder. Another thing to consider is multiplying the dividend by 10 when it becomes Smaller than the divisor, and also placing a decimal point in the Quotient.
Now, looking at the dividend, we see that we need to bring in the Decimal Point:
70 $\div$ 16 $\approx$ 4
Where:
16 x 4 = 64
Which produces a remainder of 70-64=6, and hence we move forward solving 6 as the dividend:
60 $\div$ 16 $\approx$ 3
Where:
16 x 3 = 48
Hence, a Remainder of 60 – 48 = 12 it produces, which can be used once more as the dividend:
120 $\div$ 16 $\approx$ 7
Where:
16 x 7 = 112
We can see that the Remainder produced this time can be solved as a multiple by 16, so we finish off the problem:
80 $\div$ 16 = 5
Where:
16 x 5 = 80
Hence, no remainder is produced, and we can find the Quotient to be 0.4375.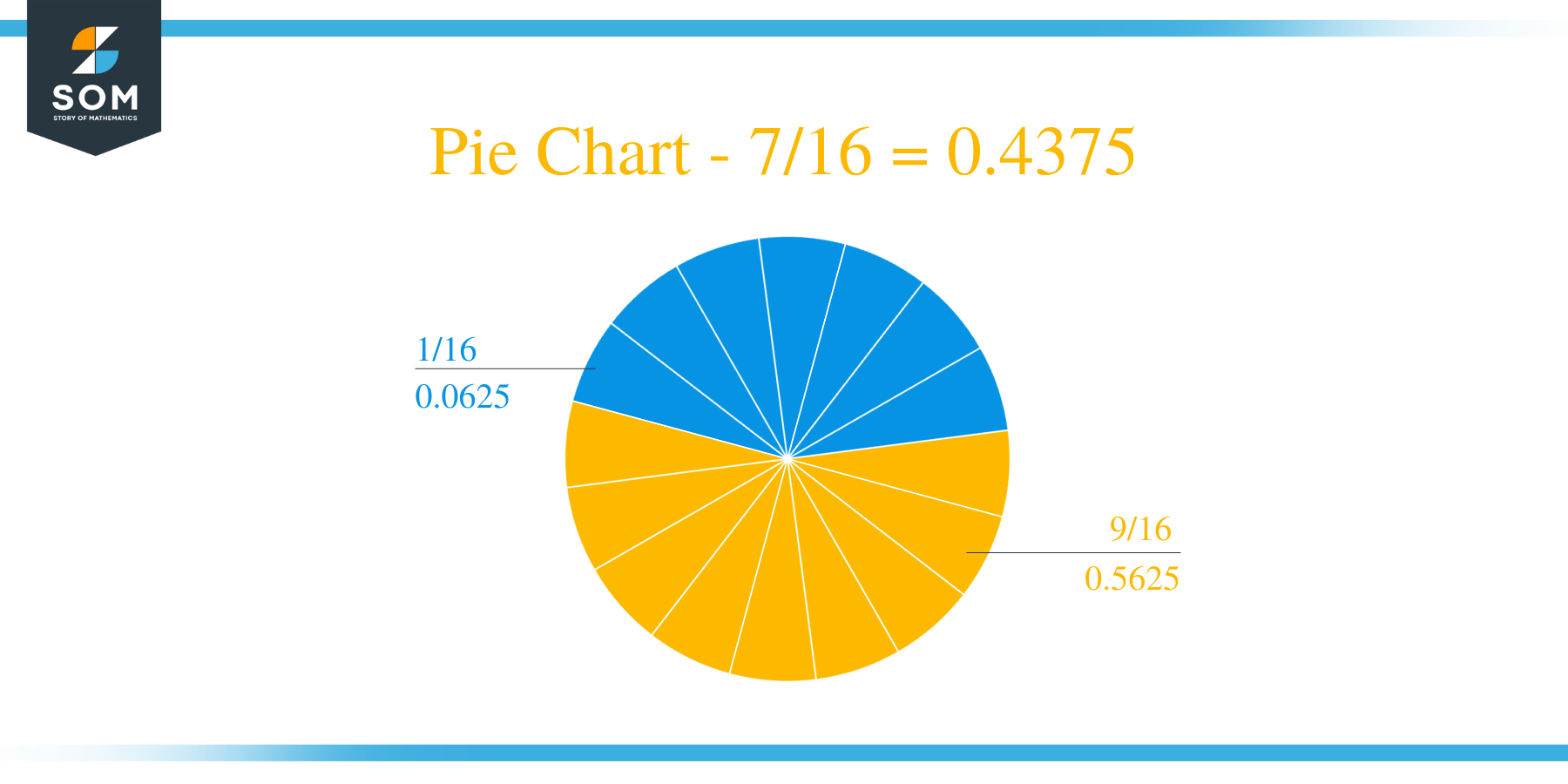
Images/mathematical drawings are created with GeoGebra.
